The labour market and distribution of income and wealth
Pineado a
362
8
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por Alvaro Ferreira6626
hace más de 9 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Alvaro Ferreira6626
hace más de 9 años
|
|

Derived demand
Aggregate demand for labour
Individual firm's demand for labour
Price of labour
Productivity
The price of other factors of production
Supplementary labour costs
The theory of marginal productivity
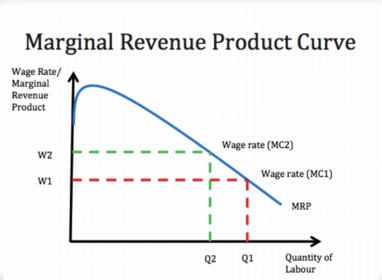
Marginal revenue product
MRP = MP x MR
Marginal product of labour
Perfect competition in the
product market=labour market
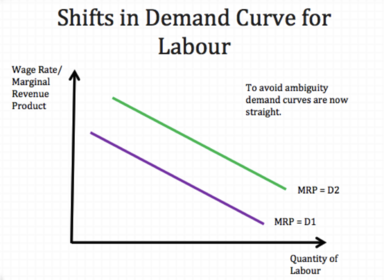
Criticisms for the theory of marginal productivity?
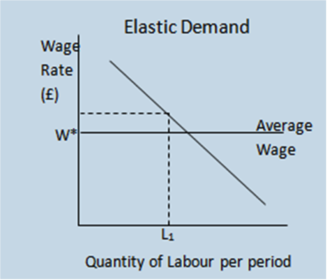
Elasticity of demand for labour
% change in QL demanded
% change in Wage rate
What determines the Elasticity of demand for labour?
Time Period
Elasticity of demand will be higher in the long run as firm could buy labour saving capital equipment
Availability of Substitutes
Elasticity of demand for the product
The proportion of labour costs to total costs
The supply of labour
Economically Active
Economically Inactive
Participation rate or activity rate
Supply of labour to a particular occupation
Monetary factors
Non monetary factors
Promotion prospects
Job security
Working conditions
Perks and fringe benefits
Net advantage
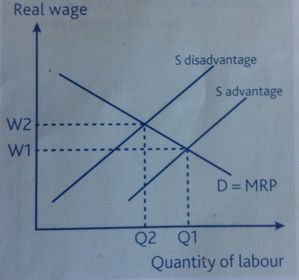
Supply of labour to a particular firm
Availability of training
Location
Level of unemployment
Opportunities for overtime work
Labour supply curve
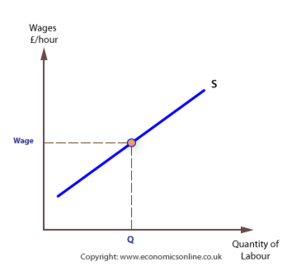
Elasticity of supply of labour
% change in Q of labour supplied
% change in wage rate
What determines the elasticity of supply for labour?
The skills and qualifications needed in the job
The length of training period
Sense of vocation
Time period
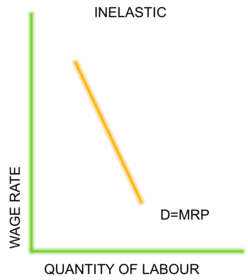
The individual supply of labour
The backward bending curve

Income effect
(Wage increase)
Substitution effect
(Wage increase)

Wage Determination
Demand and Supply
(Wage determination)
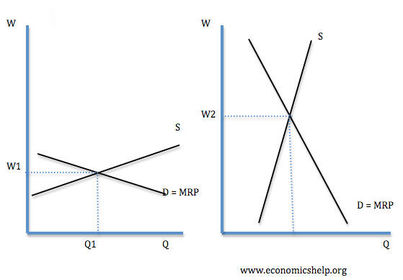
Economic rent
Transfer earnings
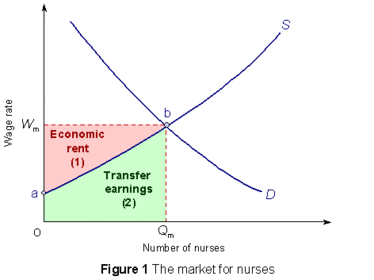
What does the economic rent depend on?
Trade union
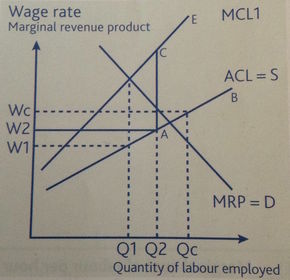
Trade union mark-up
Trade unions
Criticisms of Trade unions?
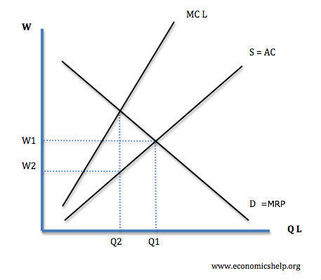
Monopsonist
Employers with labour market power
Monopsony in a market without trade unions
Monopsony in a market with Trade unions
Wage Differentials
Demand and Supply
(Wage differential)
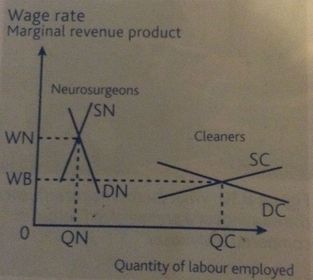
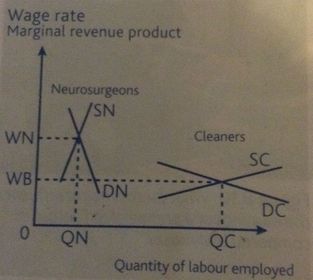
Relative bargaining strength
Government policy
Esteem
Wage differentials between particular groups
Skilled and Unskilled workers
Male and Female workers
Male and Female workers
(2)
Part time - Full time workers
Ethnic origin
Discrimination
Labour market failure
Negative discrimination
Positive discrimination
Discrimination in the labour market
Costs of negative discrimination
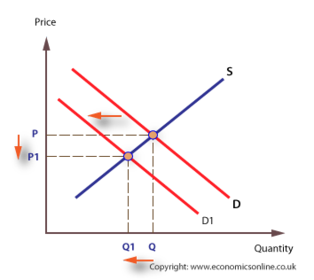
Wealth
Marketable wealth
Non marketable wealth
Distribution of wealth
UK's distribution of wealth
Wealth distribution between groups
Sources of Wealth
Inheritance
Saving
Entrepreneurship
Chance
Wealth Inequality
Marriage
Income inequality
Income
Distribution of income
How is the distribution of income measured?
(Lorenz Curve)
Gini coefficient
Lorenz Curve
(a / a+b)
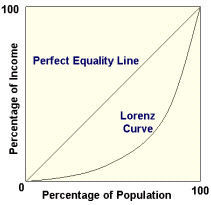
Distribution of household income in the UK has become more unequal
What causes income inequality between households?
Impact of the state
Wealth Inequality
(Cause of income inequality)
Household composition
Level of skills and qualifications
Differences in earnings
Geographical distribution of income
Reasons for unequal geographical distribution of income
Reasons for unequal geographical distribution of income
(2)
Government policies to redistribute income
Methods of government intervention
Taxation
Monetary benefits
Means tested
Universal
Direct provision of goods and services
Legislation and labour market policy
Absolute Poverty
Relative Poverty
Relative Poverty
Measuring poverty
What causes poverty?
Unemployment
Low wages
Sickness and disability
Old age
The poverty trap
Imperfect information
Government policy measures
(Poverty)
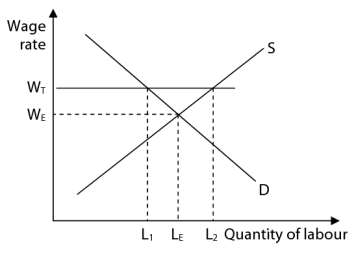
National minimum wage
Cutting the bottom rates of income tax
Training and education
Exploiting "Trickle down" effects
Increasing benefits
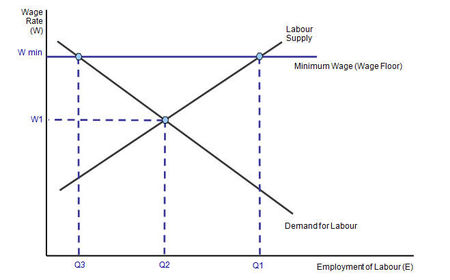
Evaluation for NMW
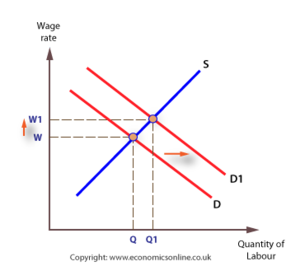

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes