A Levels Economics Fichas sobre Microeconomics year 1, creado por Nkolika Ezepue el 06/09/2015.
Pineado a
237
8
0
|
|
Creado por Nkolika Ezepue
hace más de 9 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Nkolika Ezepue
hace más de 9 años
|
|

What are the BRIC countries?
What is natural science? give examples
What is social science? Give examples.
What are the steps of applying science to economics?
What are hard laws?
What are soft laws?
What are positive statements?
What are normative statements?
What is a budget deficit? think of two ways to solve this
What are economic decisions frequently influenced by?
What are the stages of economic stability/ financial security?
What are factors of production?
What is land and what is the payment for their use?
What is labour and what is the payment made for its use?
What is capital and what is the payment for their use?
What is enterprise and what is the payment made for it?
What are consumer goods?
How does the factors of production affect overall output?
What are zero hour contracts?
Give 2 advantages of zero hour contracts
Give 2 disadvantages of zero hour contracts
What is the economic problem and what has to be made in order to approach the situation?
What is a trade off?
What 3 major problems do societies need to resolve?
Give 3 reasons why demand for NHS is increasing
What are possible solutions to this?
What is the opportunity cost?
What is 'ceteris paribus'?
What are economic systems?
What are the 3 economic systems?
What is planned economy?
What is market economy?
What are mixed economies?
What does laissez-faire mean?
What is behavioural economics?
What are capital goods?
What are consumer goods?
What are the top 5 highest populations?
What does a ppf show?
What does the line represent?
What does it mean if an economy is producing goods on the ppf line?
What other things can a ppf diagram show?
Give causes of shifts outwards in the ppf
What could cause an inward shift of the ppf line?
What is productive efficiency?
What is allocative efficiency?
Describe markets
What do we mean by a competitive market?
Finish the sentence: in economics, demand has to be...
What is market demand?
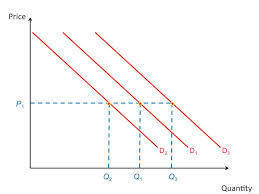
Increases in demand...
At price P1 the quantity demanded...
Decreases in demand...
At price P1, the quantity demanded
What might cause the demand curve to shift?
What are normal goods?
What are inferior goods, give an example
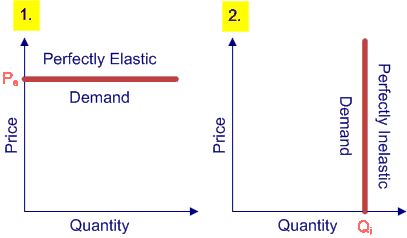
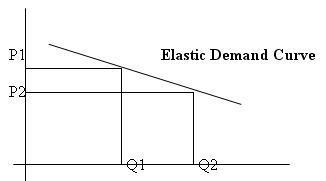
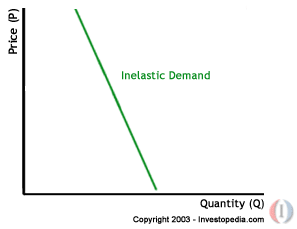
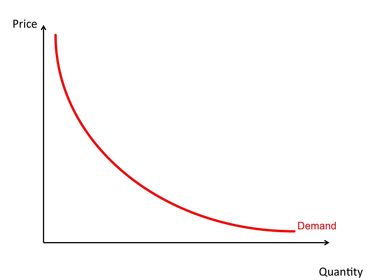
What is the law of demand?
What is price elasticity of demand?
Elastic?
Inelastic?
What determines elasticity?
How can consumer behaviourisms affect the elasticity?
The equation for PED?
What is income elasticity of demand (YED)?
Positive>1=
positive<1
negative>1
negative<1
What are complementary products?
What are substitutes?
What is cross elasticity of demand?
XED=
Substitutes are always...
Complements are always...
What is the most important determinant of supply?
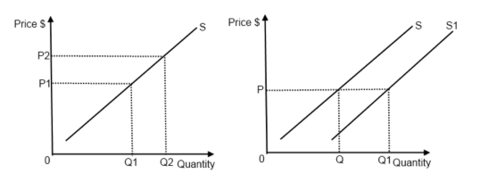
Why does the supply curve shift?
What factors cause a shift in the supply curve?
What is supply?
What is price elasticity of supply?
What factors affect elasticity of supply?
Give 3 reasons why elasticity of supply increases over time
If prices of oil rose there would be a little increase in supply (inelastic) because...
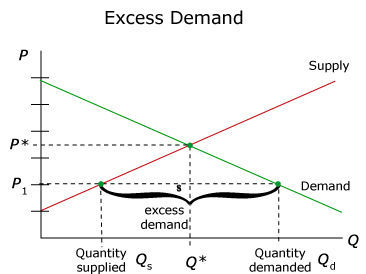
What is the equilibrium price?
What is disequilibrium?
What is excess supply?
What is excess demand?
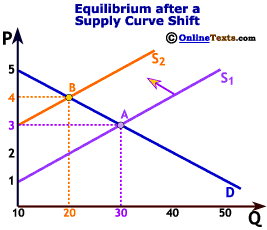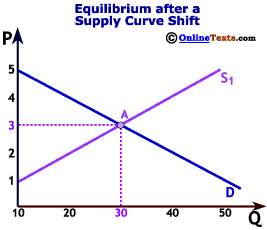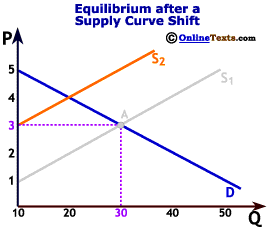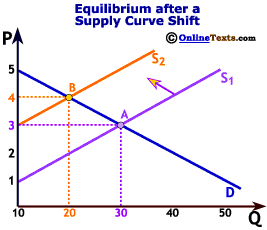
What is joint supply?
What is composite demand?
What is derived demand?
what is competing supply?
Does price affect substitutes?
What is productivity?
What are different measurements of productivity?
What are advantages of higher productivity?
What is the division of labour?
What are the benefits of division of labour?
What are the downsides?
What is specialisation?
What is our main medium of exchange?
What is bartering and what is the problem with is?
What is short run?
What is long run?
What are fixed costs and variable costs?
How do you work out total cost, average total cost?
What is the average cost curve shape, and why is it like that?
What is the shape of the AVC and why is it like that?
What is economies of scale?
What are the types of economies of scale?
How does technical economies work?
How does marketing and managerial economies work?
How does Financial economies work?
How does purchasing economies and risk bearing economies work?
What is diseconomies of scale?
What are the causes of diseconomies of scale?
What are external economies of scale?
What are the benefits of clustering/ external economies of scale?
What is clustering?
How can we compare markets?
Compare hairdressing with banking
What are the two main market structures?
What are the characteristics/assumptions of perfect competition?
Why are they so important?
Give 2 examples of prefect competition
Why are prices low in a competitive market?
What are the objectives of firms?
What are concentrated markets and give examples
What does it mean to have monopoly power?
Give 3 types of monopolies
What are natural monopolies in detail?
What are some drawbacks of monopolies?
What are the 4 factors that influence how much monopoly power a business has?
What do you mean by barriers to entry?
What do you mean by the number of competitors?
What do you mean by advertising?
What do you mean by product differentiation?
What are concentration ratios?
What are benefits of monopolies?
What do firms compete for?
What is the economic problem?
How is this problem resolved in a market economy?
What are the 3 functions of price?
What is the rationing function and give an example?
What is the incentive function and give an example?
What is the signalling function?
What do we mean by market failure and give an example?
What are the 2 types of market failure?
What are private goods?
What are public goods?
Why does the government tend to provide public goods?
What is a quasi-public good?
What is an externality?
What are positive externalities?
What are negative externalities?
What is a production externality?
Give an example of a negative production externality
Give an example of a +ve production externality
What is a consumption externality?
Negative production externality: real costs aren't reflected- should be higher so supply should be less. It's too cheap and over-produced.
Positive production externality: Costs to the consumer should be higher so supply should be higher. Its too expensive and under-produced.
What are social benefits?
What are merit goods?
Merit goods are under-provided and consumed because consumers only consider the benefits to themselves. Not the wider benefits to society.
Too few resources are allocated to the production and consumption of merit goods = partial market failure.
What are demerit goods?
How do you show demerit goods on a diagram?
The consumer over-estimates the good- willing to pay p2 etc. but in natural fact, if they took to account the real benefits, demand will fall to D1
Why might it not be so straight forward to deem a good as a merit or demerit good?
What do some economists argue the cause is for the over consumption of demerit goods and the under consumption of merit goods?
What is the root issue with the response of consumers to merit goods?
What is the root issue with response of consumers to demerit goods?
What are private costs/benefits?
What are social costs/benefits?
In what situation would you get positive or negative externalities?
How can monopolies lead to market failure?
What is immobility of labour?
What is geographical immobility of labour?
How can it be reduced?
What is occupational immobility of labour?
What is equity?
What is the distribution of income and wealth?
How can this lead to market failure?
What are free marker economists?
What are interventionist economists?
What is regulation?
How does regulation be used as a source of government intervention to correct market failures?
How does taxation be used as a source of government intervention to correct market failure?
What is the 'polluter must pay' principle?
What is a tax?
What is the price ceiling and what problems does it cause?
What is price floor?
What is gov failure?
Give some sources of government failure
What are some other sources of government failure?

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes