Cerrar

Which layer of the eye is the sclera found in?
What fraction of the eye does the sclera cover?
The sclera is anteriorly covered with x and posteriorly connected to y
What is the thickness of the sclera at
a) corneosclera
b) behind the rectus muscles
c) equator
d) posterior
Why is the sclera thickest at the back?
Where is the sclera weakest and why?
Where is the lamina cribrosa?
Why are there apertures on the anterior of the sclera?
Why are there apertures on the middle of the sclera?
Why are there apertures on the posterior of the sclera?
Where is the canal of Schlemm?
*What is the function of the canal of Schlemm?
Where is the scleral spur?
What is the funaction of the sclera?
How many layers does the sclera have?
What are the three layers of the sclera?
(From anterior to posterior)
Is the episclera loose or dense connective tissue?
Where does the episclera get its blood supply?
Does the episclera a) finish abruptly and then the stroma starts, b) form the rest of the sclera or c) merge into the stroma?
What is the innermost scleral layer?
What is the purpose of the grooves in the lamina fusca?
What separates the lamina fusca from the choroid?
Is the choroid connected to the lamina fusca? If so how?
What makes the sclera so opaque?
*What is the function of the sclera?
In which layer of the eye is the cornea found?
What fraction of the eye is civer d by the cornea?
What is the horizontal diameter of the cornea?
What is the vertical diameter of the cornea?
What is the diameter of the posterior surface of the cornea?
What is the radius of curvature of the cornea?
What is the thickness of the cornea at its
a) centre
b) periphery
*What are the functions of the cornea?
Why is the cornea transparent?
What is a) anterior to the cornea
b) posterior to the cornea?
Which structure(s) is the cornea continuous with?
How many layers are in the cornea?
Name the layers of the cornea (anterior to posterior)
How thick is the corneal epithelium
a) in cells
b) in micrometers
True or false- the corneal epithelium is continuos with the conjunctival epithelium
How many layers are there in the corneal epithelium?
Name the layers of the corneal epithelium (anterior to posterior)
How thick is the corneal surface epithelium? (In cells)
What type of cells are in the corneal surface epithelium layer?
How is the corneal surface epithelium joined to the tear film?
What type of junctions join the surface corneal epithelium cells?
Why is/isn't the surface epithelium of the cornea semi-permiable?
How many cells thick is the middle epithelium layer of the cornea?
What type of cells are in the middle cell layer of the cornea?
What joins wing cells in the corneal epithelium together?
What joins wing cells to the surface epithelium and to the basement epithelium of the cornea?
What is a desmosome?
What is a gap junction?
What is a zonula occludens?
How many layers does the besement epithelium of the cornea have?
What type of cells are in the basement layer of the cornea?
What attaches the basal columnar cells of the cornea together?
How are the corneal epithelium cells replaced?
Why is the Bowman's layer not always considerd to be a layer in the cornea?
How thick is the Bowman's layer?
Can the Bowman's layer regenerate? Why doesn't this matter?
How thick is the corneal stroma?
What percentage of the cornea is the stroma?
What type of cells are in the corneal stroma?
What are keratocytes?
What is the range of diameters for a collagen fibril (in the corneal stroma)?
True or false- fibrils in the lamellae of the corneal stroma run parallel to each other
True or false- lamellae in the corneal stroma run parallel to each other
Are the lamellae in the corneal stroma thicker anteriorly or posteriorly?
Are the lamellae in the coreneal stroma more regularly arranged posteriorly or anteriorly?
How is the corneal stroma bound to the Descements membrane?
*What is the function of the corneal stroma ground substance?
What makes the cornea transparent?
How thick is the Descements membrane?
How many lamellae layers make up the Descements membrane?
What are the features of the corneal posterior lamellae?
What are the features of the corneal anterior lamellae?
How thick is the corneal endothelium?
What is posterior to the corneal endothelium?
Which surface of the corneal endothelium lies on the Descements membrane?
What shape are the majority of the corneal endothelial cells?
Are corneal endothelial cells arranged regularly to irregularly?
Do the corneal endothelial cells divide?
How are the corneal endothelial cells joined together?
Is the corneal endothelium permeable?
How is the corneal endothelium hydrated?
How does the cornea receive nourishment?
Where are the nerves in the cornea?
Where is the limbus?
Which structures terminate at the limbus?
The limbus is the transitional zone between which two pairs of structures?
What does the a) corneal epithelium become at the limbus, b) regular corneal stroma, c) corneal endothelium ?
Which three structures begin at the limus?
How thick is the limbal epithelium?
Why are some peoples limbi pigmented?
Where is the scleral spur?
What are the Palisades of Vogt?
*What is the function of the Palisades of Vogt?
What makes up the limbal blood vessel network?
Where do the limbal veins drain?
*What are the two main functions of the limbus?
Which two structures is the iris suspended between?
What is the iris?
*What is the function of the pupil?
What is the name of the termination of the iris?
Where is the pupillary margin?
Where is the iris a) thickest, b) thinnest?
What is the diameter of the iris?
What produces the iris colour?
Which colour of iris has the a) most melanin granules, b) least melanin granules?
What is the diameter of the pupil?
When is the iris a) miotic, b) mydriatic?
What are the two main surfaces of the iris?
Where is the colarette? Describe its features.
What causes the appearance of the concnetric and contraction furrows?
Where are they located?
Does the iris have an epithelium?
What makes the ruff?
Describe the appearance of the posterior surface of the iris.
Where are the radial contraction furrows of Schwalbe located?
What are the histological layers of the iris?
What cells and fibrils make uo the anterior border layer of the iris?
Does the anterior border layer cover the iris?
Where does the anterior border layer of the iris terminate?
What is the iris stroma?
What cells are pigmented in the iris stroma?
What are the non-pigmented cells in the iris stroma?
Where is the sphincter iris muscle?
What type of muscle makes up the sphincter iris muscle?
*What is the function of the sphincter iris muscle?
Is the sphincter muscle of the iris innervated by the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system?
Name the layers of the anterior iris epithelium.
What type of cells make up the apical portion of the anterior epithelium?
What makes up the basal portion of the anterior epithelium?
Where are the boundaries of the dilator muscle of the iris?
How is the iris dilator muscle of the iris arranged in comparison to the iris sphincter muscle?
What type of muscle makes up the dilator muscle of the iris?
*What is the function of the dilator muscle of the iris?
Is the dilator muscle of the iris innervated by the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous system?
*What is the function of the iris?
What makes up the posterior (second posterior) epithelium of the iris?
Why are the anterior and posterior iris epithelium layered apex to apex?
What are heterochromia and pigmentary dispersion syndrome?
Where does the arterial supply of the iris come from?
Where does the venous supply of the iris come from?
Why are the veins and arteries associated with the iris spiraled?
Which nerves supply the iris, and what specifically do they innervate?
In which layer of the eye is the iris found?
In which layer of the eye is the choroid found?
Outline the dimensions of the choroid and its boundaries.
Describe the inner and outer surfaces of the choroid (hint: take into account the layers that surround the choroid).
Where is the perichoroidal space?
Which two sheaths does the choroid become continuous with at the optic nerve?
Lable the diagram

Name the layers of the choroid.
Name the cells and the types of blood vessels in the blood vessel layer of the choroid.
Where do the arteries and the veins in the vessle layer of the choroid come from/go to?
What type of blood vessles are in the choriocapillaris? Where are they most concentrated and why?
Where do the capillaries in the choroid a) get their blood supply from and b) drain into?
How many layers are in the Bruch's membrane? What are they called?
*What is the function of the Bruch's membrane?
What is the main blood vessel that supplies the choroid with blood?
Which blood vessels drain the choroid?
How is the choroid innervated, and where do the nerves enter the eye?
*What is the function of the choroid?
In which layer of the eye is the ciliary body found?
Outline the dimensions of the ciliary body and its dimensions.
Lable the diagram
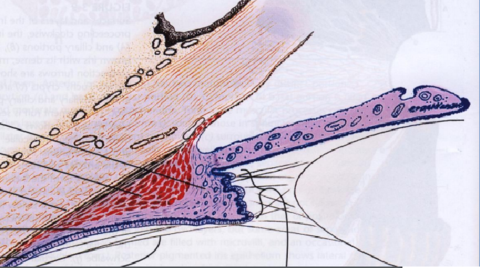
What shape is often associated with the ciliary body? Which ocular structures do the parts of this shape lay nearest to?
Which two parts make up the ciliary body?
What are the other names for the pars plana and the pars plicata?
What are the dips inbetween the pars plicata's processes called?
What are the boundaries of the pars plicata?
What are the boundaries of the pars plana?
What are the portions inbetween the pars plana called?
What are the zonula fibres?
How many layers are in the ciliary bidy? What are they called?
Describe the position of the supracilliaris.
Describe the features of the surpacilliaris (what it contains and its arrangement).
What type of muscle makes up the ciliary muscle? How is this muscle orientated?
Lable the diagram
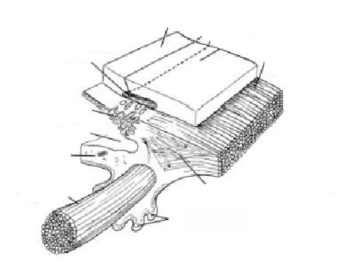
Where is the insertion of the longitudinal ciliary muscle of Brücke?
Where are the radial fibers of the ciliary muscles? Where do they originate from?
At the radial fibres the type of muscle fibre transitions from a) to b)
What is Müllers annular muscle? Where is it located?
Which branches of the nervous system innervate the ciliary muscle?
Describe the ciliary stroma in relation to blood vessels, the type of connective tissue, its location *its function and the layers that it is continuous with.
Where is the major arterial circle of the iris?
How many layers of ciliary epithelium are found in each eye? How are they postioned?
Describe the outer layer of the ciliary epithelium.
Describe the inner layer of the ciliary epithelium.
*What is the function of the ciliary body?
*What is the function of the ciliary muscles?
How many layers are in the retina? What are there names (in order)?
What is the function of the retina?
What are the three main regions of the retina?
What is the retinal pigmented epithelium?

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes