Cerrar

Explain why although the bonds between atoms in a simple covalent compounds are strong, simple covalent compounds are usually found as gases ?
Why do substances that consist of simple molecules eg CO2 not conduct electricity ?
Explain why ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points ?
Explain why ionic compounds can conduct electricity when melted or dissolved ?
Explain why giant covalent structures or macromolecules e.g. diamond , graphite, silicon dioxide have high melting points ?
What is the name of this covalent macromolecule?
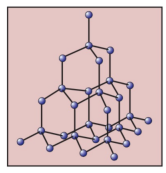
What is the name of this covalent macromolecule?
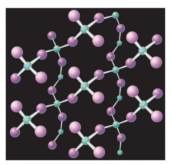
What is the name of this covalent macromolecule?
How many bonds does carbon form with other carbon atoms in diamond ?
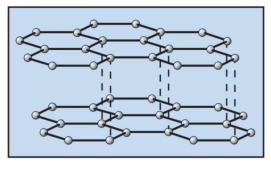
Explain why graphite is soft and slippers ?
What type of bonding do you find between the layers in graphite ?
Fullerenes are based on what shape of
rings of carbon atoms.
Give 4 uses of fullerenes.
Explain how graphite is similar to a metal ?
Explain why metals are good conductors of heat and electricity ?
Explain why most metals can be bent and shaped ?
Why are alloys stronger than pure metals ?
What are shape memory alloys and give an example ?
Explain why low density and high density poly(ethene) have different properties.
Explain the properties of thermosoftening polymers in terms of intermolecular forces.
Explain why thermosetting polymers do not melt when heated.
State the main property of LD polyethene and list 2 of its uses.
State the main property of HD polyethene and list 2 of its uses.
Describe the reaction conditions used to make LD polyethene
Describe the reaction conditions used to make HD polyethene
Describe what nanoscience structures refer to
Describe the relationship between surface area and volume in nanoparticles
List 6 uses of nanoparticles

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes