Fichas sobre Chemistry 11: Matter, Chemical bonding and Chemical Trends, creado por Alex Obray el 11/12/2015.
Pineado a
221
3
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por Alex Obray
hace casi 9 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Alex Obray
hace casi 9 años
|
|

1. What is matter? Draw a diagram of the classification of matter
2. What are pure substances?
What are they referred to as in chemistry?
3. What are mixtures?
What are homogenous mixtures referred to as in chemistry?
4.What is an atom and what makes up an atom?
5. What determines an atom?
6. What is an ion?
7. What does the atomic number correspond to and what is it represented as?
What can it also respresent?
8. What is the mass number and what is it represent as?
9. The number of neutrons in a given atom can be calculated using the formula
10. Iron has an atomic number 26. Its mass number is 56. The number of neutrons it contains is:
11. What is an isotope?
How are they named?
12. The element carbon has 3 isotopes: carbon-12, carbon-13 and carbon-14. How many neutrons do they have?
13. What element has the most amount of isotopes?
14. What does the nucleus determine?
15. What is C-13?
What is C-14?
16. How do the properties of isotopes compare to one another (e.g. isotopes of carbon)?
17. Why is the average mass of carbon not the mean of 12 + 13?
18. There are two isotopes of helium in the sample, representing the distribution of helium on this planet: There are three He-4 atoms for ever He-8. What is the relative atomic mass of helium, as measured in atomic mass units?
19. Carbon exists in two forms: C-14 and C-12. Which statement is true of carbon?
a) C-12 forms carbon monoxides and C-14 forms carbon dioxide
b) the atomic mass of carbon must be more than 12
c) C-14 is more reactive than C-12
d) Both forms of carbon have the same number of neutrons
e) none of above
20. Random sample of element has 75% of its atoms weighing 35 and 25% weighing 37. What is the relative atomic mass?
21. Which of the following is an ion?
A) C
B) I2
C) HIO3
D) IO3-
22. How many neutrons are there in a silver atom? (silver has an atomic number of 47 and a mass number of 108)
a)47
b) 61
c) 94
d) 155
23. Which of the following is a heterogeneous mixture?
a) distilled water
b) rubbing alcohol
c) soil
d) apple juice
24. CO2 can be classified as a (an):
atom
molecule
mixture
solution
25. What is the safety system called?
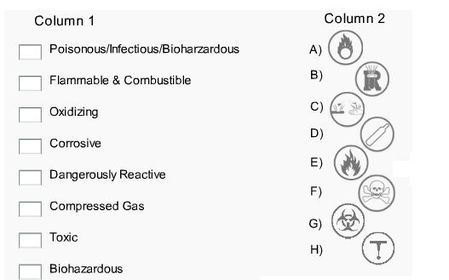
26. What do these symbols represent?

27. Elaborate

28.

29. What is MSDS?
30.
31.

32.

33.

34.

35.

36.
37.

39. How long has the periodic table been around for?
40. Who organized the periodic table in almost the way we view it today and when?
41. What are the columns and the rows of Mendeleev's periodic table called?
42. What is the the periodic table of the elements? What is the periodic law?
43. How many families is the periodic table divided into?
44. In what general area are the metals located on the periodic table?
left
right
top row
in the middle
45. Where are the halogens located on the periodic table?
group 1
group 2
group 17
group 18
46. Where are most of the gases located on the periodic table?
left
right
middle
top row
47. In what general area are the non-metals located on the periodic table?
left
right
top row
only in the middle
48. Has any elements been discovered by Canadians?
49. Where are electrons found in an atom?
What indicates the energy levels of an element on the periodic table?
50. Where are electrons with higher energy located in an atom? Who proposed this? Is there a limit?
51. How many electrons can H and He have in their energy level?
What about elements 3 to 20?
52. What is the name for electrons located at the highest energy level? What do they determine?
53. What is a general rule you can use to determine an atom's valence electrons?
54. Although properties for elements within a column in the period table are similar, what differs? What is it called?
55. List the elements of the activity series
56. How much gold has been obtained by humans?
57. Elaborate on alkali metals regarding to reacting to air
What can you tell you about the activity series for the alkali metals?
58. How do alkali metals such as lithium and sodium react with water?
59. How do potassium, rubidium and cesium react with water?
60. Do metals react with water?
61. What type of acids react with metals and what do they liberate?
62. What occurs when a metal (e.g. a coin) interacts with a solution made of a metal lower in the activity series?
What occurs in an opposite situation?
63. Which of the following is a metal?
carbon
vanadium
fluorine
xenon
64. Which of the following is a metalloid?
carbon
phosphorus
tin
antimony
65. A chemist is working with four substances: nitric acid, silver, magnesium and aluminum. Which one of these is the most reactive?
nitric acid
silver
magnesium
aluminum
66. How many valence electrons are there in a carbon atom?
67. What is a period trend? (First, relate it to valence electrons, then define it)
68. What are the most common trends of the periodic table?
69. What are alkali metals?
70. What are alkaline earth metals?
71. What are transition metals?
72. What are lanthanides?
73. What are actinides?
74. What are halogens?
75. What are rare gases?
76. What are metalloids?
77. What is a chemical bond and how many bonds can an atom have between them?
78. The human body is capable of manufacturing many molecules, some for survival and others as waste. It is capable of producing molecules with millions of bonds, but what is type of molecule is the body in capable of producing?
79. What is the octet rule?
80. What is an ionic bond?
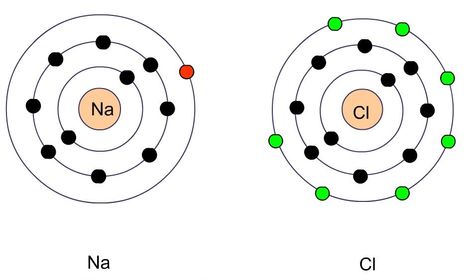
81. Example relating to ionic bonds: Sodium has its 11 electrons arranged in three energy levels. Closest to the nucleus will be the first level containing 2 electrons, then the second level containing 8 electrons, leaving 1 electron in the outermost energy level. What is the easiest way for sodium to gain a stable electron configuration?
82. Chlorine has 17 electrons, 7 of which are in its outermost energy level. How can it gain a stale electron configuration?
83. What is the most polar type of bond?
84. Do ionic bonds form a molecule?
85. What is this resultant of sodium and chlorine interacting?
86. What is a covalent bond?
87. What is a polar bond?
88. What is a non-polar covalent bond?
89. What is a polar covalent bond?
90. What is a covalent compound called?
91. What is molecular polarity dependent on?
92. How can you determine the type of bond occurring between two atoms?
93. What can a bond spectrum table be used to predict?
94. Write the bond spectrum table for covalent (non-polar) bonds being the most probably type
95. Asenic has an electronegativity of 2.0 and selenium's is 2.4. What type of bond is between these atoms?
96. The bond that forms between a calcium atom and a bromine atom is:
a) ionic
b) polar covalent
c) non-polar covalent
d) a hydrogen bond
97. a) ionic
b) polar covalent
c) non-polar covalent
d) a hydrogen bond
98. What are the properties of ionic compounds?
99. What are weak interactions?
100. What are intermolecular forces?
101. When was dispersion forces first described?
What about for dipole-dipole interactions?
102. Why do metals and ionic compounds have extremely high melting and boiling points?
103. All molecules have the capability to form what type of force?
104. What are dipole-dipole forces?
105. What is hydrogen bonding?
106. Only one of the following lists does not consist entirely of symbols for elements. Which one?
a. C, He, Mg, Cu
b. H, ASA, P, Fe
c. He, N, Cl, O
d. Ca, Ne, Fe, He
107. The correct association of the following pairs of terms is given by:
a. families are to periods as rows are to groups
b. periods are to rows as families are to columns
c. rows are to families as groups are to families
d. columns are to periods as rows are to families
108. Element number 92 is a:
a. gas
b. metal
c. metalloid
d. non-metal
109. Which of the following groups of elements contains only metalloids?
a. Ge, As, Sb, Si
b. Li, Na, K, Rb
c. Ge, As, Ni, W
d. Ge, Pb, Au, Ag
110. 6. In the modern periodic table, elements with similar properties appear in the same row.
a. true
b. false
111. Most of the known elements are metals.
a. true
b. false
112. The noble gases are very reactive elements.
a. true
b. false
113. Elements in the same column have the same number of valence electrons.
a. true
b. false
114. Potassium belongs to the group of elements known as halogens.
a. true
b. false
115. In the periodic table, elements with similar chemical properties are found in ______
116. Elements that possess some properties of metals and some properties of non-metals are called ____
117. The number of electrons in an atom is the same as the number of ____
118. In what region of the periodic table are the non-metals found?
119. How many valence electrons does an atom of strontium have?
120. What determines the order of elements in the modern periodic table?
121. State the periodic law. With reference to the physical and chemical properties of the alkali metals, show how this family of metals illustrates the periodic law.
122. Electronegativity trend
123. Atomic Radius Trend
124. Ionization energy trend
125. Electron Affinity Trend
126. Metallic Character Trend
127. In the periodic table, elements that have similar properties are grouped in horizontal rows.
True or False?
128. Of the elements He, Fe, S, Ca, and K, the one that would react in a way that is most like Na is Ca.
True or False?
129. Which of the following elements is the largest in size?
Question 7 options:
A) O
B) He
C) K
D) H
130. With respect to their location on the periodic table, the elements having the greatest tendency to loose an electron are found
Question 8 options:
A) upper left
B) lower left
C) upper right
D) lower right
131. As the atomic number increases within the alkali metal family, ionization energy
Question 10 options:
A) increases and atomic radius increases
B) increases and atomic radius decreases
C) decreases and atomic radius increases
D) decreases and atomic radius decreases
132. Which of the following elements tends to hold onto its outer electrons most strongly?
Question 11 options:
A) He
B) Na
C) K
D) Ne
133. Briefly state the following trends:
As the atomic number increases, ionization energy in a period
134. Briefly state the following trends:
As the atomic number increases, atomic radius in a period
135. Briefly state the following trends:
As the atomic number increases, atomic radius in a family
136. How do you determine which substances are least ionic?
137. What is a lewis structure?
138. What does a The Lewis structure of a compound show?
What is used instead of using two dots for two electrons?
139. Show the Lewis structure for water
140. What are exceptions to the octet rule?
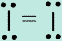
141. The Lewis structure for I2 is
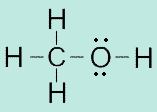
142. The Lewis structure for CH3OH is
143. The Lewis structure for HCN is
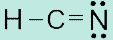
144. What do chemical formulas exist?
What information do they provide chemists with?
145. What does an atom's valence indicate?
146. What is a binary compound?
How do you name a binary compound?
147. When writing and naming a binary compound, which element is written first?
How many valence possibilities do single valence ions have?
148. Give a few example of valence possibilities for multiple valence ions.
149. Fe2+ is...
Fe2+ is called...
Fe3+ is called...
150. The chemical FeO is made up of Fe2+ and O2-
What is its name and old name?
151. What are the general rules for writing binary compounds?
152. What is a tip for binary compounds relating to subscripts?
153. What is the chemical formula for the compound formed from Na and I?
154. What is the chemical formula for the compound formed from zinc and bromine?
155. What is the chemical formula for the compound formed from lead(IV) and oxygen?
156. For binary covalent compounds (two non metal elements combining), the number of the most electronegative element is preceded by the Greek prefix corresponding to that number. Below is a list of these Greek prefixes.
What are the prefixes from 1 to 10?
157. What is the valence of the element?
What does the valence number refer to?
158. Explain a fluorine atom becoming an anion.
159. What is an ionic compound?
How do we figure out how various atoms will combine to form ionic compounds?
160. What is the name of CuBr2?
161. What is the name of Al2O3?
162. What is the name of RbCl?
163. What is the name of N2O?
164. What is a binary acid and how do you name it? e.g. HCl
165. How do you name a ternary (3 elements) ionic compound? e.g. HClO3
166. How do you name a ternary (3 elements) ionic compound for HNO2 and H2SO3
167. Are acids ionic? Why?
168. What is a polyatomic ion? e.g. NH4(+), CO3(-2)
169. What is a polyatomic compound and what are the general rules for writing polyatomic compounds??
170. What are oxyacids?
171. What are derivative oxyacids?
172. The main oxyacid containing H, Cl and O is HClO3 and is called chloric acid. What would be the name of the oxyacids with one oxygen atom is removed, two oxygen atoms are removed and one oxygen atom is added to the main oxyacid?
173. What is the name of H2CO3?
hypocarbonous acid
carbonous acid
carbonic acid
percarbonic acid
174. HClO2 is called hypochlorous acid. True or false.
175. What is the chemical formula of persulphuric acid?
HSO3
H2SO3
H2SO4
H2SO5
176. Hypophosphorous acid is:
H3PO
H3PO2
H3PO3
H3PO4
H3PO5
177. When the hydrogen from an acid is replaced by a metallic element, a salt is formed.
What are the rules for naming salts formed from oxyacids? e.g. nitric acid (HNO3)
178. What is the chemical formula for chromium (II) bicarbonate?
179. What is the chemical formula for lithium hypochlorite?
180. What is the chemical formula for sodium hydroxide?
181. What is the name of CuSO4?

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes