All of the nauro-anatomy included in my first year Biology module at UoN.
Pineado a
337
19
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por Rachael Jones
hace más de 8 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Rachael Jones
hace más de 8 años
|
|

Name the 4 locational terms for the brain (above/below/in front/behind)
Define Medial and Lateral.
How many ventricles are part of the Ventricular System. (describe anatomy)
Name the three techniques of slicing the brain.
What is a Myelin? (for example the corpus callosum).
What is grey matter?
What is white matter?
What are meninges?
What is the function of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF).
How do the capillaries in the brain differ from the capillaries of the rest of the body? (blood-brain barrier)
Name the main structures of the Fore-Brain (Prosencephalon) (2).
Name the main structures of the Mid-Brain(2).
Name the main structures of the Hind-Brain (Rhombencephalon) (2).
Define Gyri and Sulci.
Name the major nuclei of the Telencephalon(3)
Name the major nuclei of the Diencephalon (2).
Name the 2 major structures of the Metencephalon.
Name the 3 major structures of the Basal Ganglia.
Name the 5 major structures of the limbic system.
Function of the Basal Ganglia?
Function of Limbic System?
Function of the Thalamus and the Hypothalamus?
Functions of the Tectum?
Functions of the Tegmentum?
Functions of the Pons and Cerebellum (2 parts of the Metencephalon).
What are neurons? - and 3 different types of neuron?
Between structures- define Afferent and Efferent.
Describe Glia (including Astrocytes, Ogliodendrocytes, and Microglia).
Define membrane potential.
What is an ion channel?
Define ions, and 2 types of ion.
Describe resting potential.
Describe action potential.
Define depolarisation and hyperpolarisation.
The stages of Action Potential (changes in polarisation).
Define Saltatory Conduction.
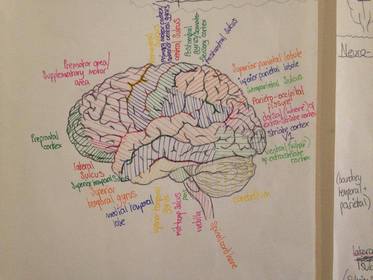
The 'groove' that separates the temporal and frontal lobes?
The 'groove' that separates the Parietal and Occipatal lobes?
The 'groove' that separates the Frontal and the Parietal lobes?
Tripartite Synapse?
What are Ionotropic receptors & Metabotropic receptors.
Define 'Excitatory Neural Integration' and 'Inhibitory Neural Integration'.
What are amino acids?
What do the poisons Curare and Muscarine do?
What is Acetycholine (ACh)
V1 visual processing is mediated by 2 streams:
Milner & Goodale * patients with occipito-temporal brain damage
Describe Face Cells
Describe the Medial Temporal Lobe (MTL)
Describe the function of the Amygdala.
Describe Kluver-Bucy syndrome
Describe the Ventromedial Prefrontal Cortex (orbitofrontal cortex)
The Parietal Lobes split into 3 main parts:
Describe the main role of the somatosensory cortex
Describe plasticity and phantom limbs
Describe the role of the superior parietal lobule
Describe the role of the inferior parietal lobule
Damage to the left posterior inferior parietal lobule?
Differences between Unilateral and Bilateral damage to the posterior parietal lobules.
What 3 landmark areas can the Frontal lobe be split into?
Describe the function of the primary motor cortex
Describe function of Premotor area/ Supplementary motor area
Describe function of Prefrontal Cortex
Properties of Schizophrenia
Describe the Dopamine Hypothesis (Pharmacology of Schizophrenia)
What is Anhedonia?
Describe Bipolar Disorder and Unipolar Disorder
Rosenthal (1971) genetic inheritance
Gershan et al. (1976)
(Affective Disorders)
Monoamine Hypothesis (pharmacology of Affective disorders)
Broca's area & Broca's Aphasia
Wernicke's area and Wernicke's Aphasia
A model of language processing?
Conduction Aphasia
Define types of memory: episodic, semantic, working, procedural, & perceptual.
Memory described as Declarative and Non-Declarative
Describe Korsakoff's syndrome
What is a Temporal Lobectomy
The role of the hippocampus
The hypothalamus' role in sleep?
The role of the Reticular system in sleep - Mouzzi & Morgan (1949)
Hetherington & Ranson (1940) (ventral medial H)
Anand & Brobeck (1951) (lateral H)
What is a sodium-potassium pump?
What is repolarisation?
How will people with frontal lobe damage perform in the stroop task?
Describe EEG patterns through stages 1-4.
What are simple cells?
Describe the fluctuation of voltage during action potentials
Describe what happens as an action potential reaches the pre-synaptic terminal.
what is the most abundant excitatory NT in the CNS.
what is the most abundant inhibitory NT in the CNS
Bechara et al. (2000) Iowa gambling task
What is the function of the ventricular system?
Define:
*a commissure
*retino-topic map
*V1 modules
*What parts of the brain constitute the visual association cortex?
*auditory association cortex?
What components are part of the Papez circuit?
Brodmann's areas?
What is the Insula (part of the brain) responsible for?
Joseph LeDoux states that...(emotional processing)

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes