Fichas sobre Chemistry unit C3 OCR Board, creado por absaroke el 08/03/2016.
Pineado a
13
1
0
Sin etiquetas

|
Creado por absaroke
hace más de 8 años
|
|
Cerrar

|
Creado por absaroke
hace más de 8 años
|
|

a) what does rate of reaction measure?
b) what part of a reaction is the fastest at generating product?
c) which part is the slowest?why?
a) what are the units for measuring the rate of reaction?
b) when is the shorter unit of time used?
a) how can rate of reaction be calculated?
b) graphically?
a) what is a limiting reactant?
b) what does directly proportional mean in terms of limiting reactant?
a) interpolation
a) why are successful collisions limited in a reaction where the number of reacting particles are limited?
a) which four things increase the rate of reaction?
a) how does temperature increase rate of reaction?
a) how does concentration increase rate of reaction?
a) how does Surface area increase rate of reaction?
a) how do catalysts increase rate of reaction?
a) How does increasing the pressure affect rate of reaction?
b) which phenomena is it similar to?
a) On a graph you know a reaction has stopped because?
b) In a table you know a reaction has stopped because?
a) How can rate of reaction be compared in a graph and a table?
a) what can combustible powders cause?
a) why are powders highly explosive? (3)
a) What 4 things are needed for a dust explosion?
a) Name any 3 combustible powders?
a) how can you increase the surface area of a substance?
a) why will a powdered form of a substance have a greater rate of reaction than a block form of a substance?
a) What does RFM stand for?
b)why is it significant?
c) Which number in the periodic table of elements gives the RFM of any particular element?
a) What is the relative formula mass of Ca(NO3)2 ?
When RFM of Ca= 40, N=14 and O=16
a) what is the principle of conservation of mass?
b) what does it mean literally?
a) how do you prove the conservation of mass?
a) Prove the conservation of mass in this reaction?
CuCo3 -> CuO + CO2
when Atomic masses are
Cu = 64, C = 12, O = 16
a) If you had 124g of CUCO3 in the reaction
CuCo3 -> CuO + CO2
how many grams of CuO would you make?
a) If you had 24.8g of CUCO3 in the reaction
CuCo3 -> CuO + CO2
how many grams of CuO2 would you make
a) How do you Calculate percentage yield?
a) Show that mass is conserved in the reaction:
ZnCO3 -> ZnO + CO2
if RFM of Zn = 65, C = 12 and O =16
a) A soap manufacturer calculates the yield required to be 150 tonnes. However when the product is made only 147.6 tonnes have been produced. Calculate the percentage yield
a) In the reaction
2HgO -> 2Hg + O2
0.069g of O2 was formed at a percentage yield of 93. 2%, what was the theoretical / predicted yield?
a) What is percentage yield?
a) What is 'theoretical yield'?
b) Why is this rarely / never achieved? (3)
a) Why do Industrial processes need / want to have a high percentage yield?
a) How is atom economy calculated?
a) A company makes potassium nitrate for fertiliser and rocket propellant in fireworks. H2O is the waste product, what is the atom economy of the reaction:
KOH + HNO3 -> KNO3 +H2O
a) Iron ore can be reduced to iron using the reaction:
Fe2O3 + 3CO -> 2Fe +3CO2
CO2 is the wasted product, what is the atom economy of this process?
a) Zinc oxide can be made by this reaction:
ZnCO3 -> ZnO + CO2
CO2 is the waste product. ZnO is the desired product. Calculate the atom economy for this reaction.
a) Why does Industry want the highest atom economy possible?
a) This is the reaction in which asprin
( C9H804 ) is made:
C7H603 + C2H3OCl -> C9H8O4 +HCL
what is the atom economy of making asprin?
a) A reaction absorbs heat from its environment is?
b) Give an example process? Why?
c) Example of an object?
a) A reaction which gives out heat is?
b) Give an example process? Why?
c) Example of an object?
a) How do you decide if a reaction is endothermic or exothermic?
a) Diagrams can be used to represent bond energy changes, what would a diagram showing an overall exothermic reaction look like?
a) Diagrams can be used to represent bond energy changes, what would a diagram showing an overall endothermic reaction look like?
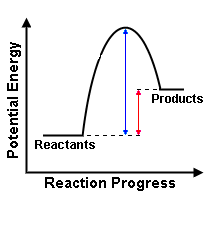
a) Label the diagram and state which kind of reaction it shows?
b) What is happening in each stage?
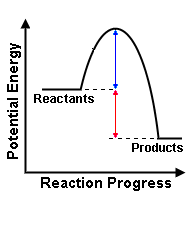
a) label the diagram and state which kind of reaction it shows?
b) What is happening in each stage?
a) How do you calculate the energy transferred by a fuel in j?
a) what is the specific heat capacity of water?
b) how can you find the mass of burned fuel during an experiment?
a) To find out the energy released by 1 gram of fuel?
a) How is the energy released per gram of fuel calculated?
a) How could you compare the energy released when different liquid fuels burn?
a) What is batch production in industry?
a) Give examples of products made in a batch process? (4)
a) What are the advantages of batch production? (6)
a) What are the disadvantages of batch production? (5)
a) What is the cycle of batch production? (5)
a) What is continuous production in industry?
a) What are the advantages of continuous production? (4)
a) What are the disadvantages of continuous production? (4)
a) Give examples of products made in a continuous process? (6)
a) Why is it difficult to develop and test new medicines? (6)
a) Why are medicines so expensive? (5)
a) What mass of carbon would you need to burn, in excess oxygen to make 84g of carbon dioxide?
a) What does a graph of rate of reaction look like?
a) what is collision theory?
b)How does collision theory explain rates of reactions
a) How are chemicals extracted from plants?
a) What is chromatography?
b) What is the difference between chromatography and thin layer chromatography?
a) How can the purity of certain compounds be tested?
a) Why is it difficult and costly to get a licence for a new drug? (6)
a) What are Allotropes?
b) Can you give an example?
a) What are Moles for?
b) What is one mole equal to?
a) What are fullerenes?
b) what can they be used for?
c) give an example of a fullerene used in this way?
a) How many atoms are there in buckminsterfullerene? what kind are they?
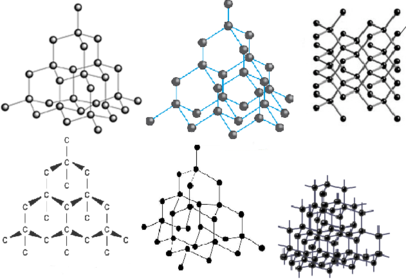
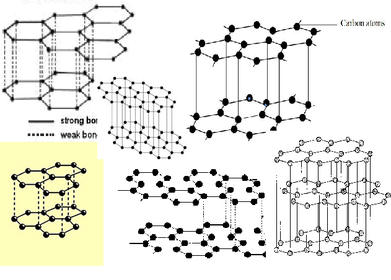
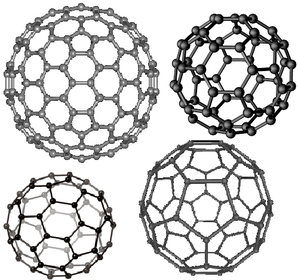
a) What is the formula of buckminsterfullerene?
b) what is each buckminsterfullerene structure measured in?
a) What are covalent bonds?
b) what are the 2 types of covalently bonded substances?
a) What is the difference between
simple covalent bond molecules and giant covalent structures/ macro covalent structures?
a) Why can't diamond conduct electricity when graphite, another allotrope of carbon can?
a) How many particles are there in 1 mole of any atom?
b) what is the formula triangle for mole to grams to RFM calculations?
a) What is the RFM of a compound that weighs 266g if i have 4.75 moles?
b) Calculate the number of moles of carbon dioxide molecules in 22 g of CO2.
a) What would the mass of 2.5 moles of NH3 be?
a) What Kind of structure of carbon are diamond, fullerenes and graphite?
b) Why is diamond used in drill bits?
a) How are carbon atoms joined in diamonds?
a) Why is diamond used in Jewellery?
a) What can graphite be used as?
b) Why?
a) what is the melting point of diamond?
a) what an you use as a catalyst system?
a) How are carbon atoms joined in graphite?
a) What does giant covalent bonding form?
b) What will happen if a structure like this forms bonds in different directions or has de-localised electrons?
c) What will happen if a structure like this forms bonds in layers?
a) What are the issues with Patents for drug manufacturers?
a) What is nano-technology?
b) How does sunscreen use nano-technology?
a) How small is 'Nano' ?
b) How do car airbags use nano-chemistry?
a) What are the uses of nano-chemistry? (5)
a) What are the safety concerns of nano-technology?(4)
b) Who would be most at risk of any potential dangers?
c) how could the risks be reduced?

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes