Flash cards that can help to test your understanding of B1.
Pineado a
20
1
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por Molly Bradbury
hace más de 8 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Molly Bradbury
hace más de 8 años
|
|

What are the six types of fitness?
List the factors that increase the risk of heart disease
Why is blood in the arteries under pressure?
What is your BP?
What is it measured in?
What is your Systolic pressure?
What is your Diastolic Pressure?
What does healthy mean?
What does it mean if you are fit?
List the factors that increase blood pressure
Explain how smoking increases blood pressure
How could you decrease blood pressure?
What are carbohydrates made up of?
What are proteins made up of?
What are fats made up of?
The equation to calculate BMI is;
What is your EAR?
The equation to calculate EAR for protein is:
EAR QUESTION;
Sue is 72.5KG. What is her EAR?
BMI MEANINGS;
What is the name for protein deficiency and why is it common in developing countries?
A women is 1.72m and 62kg
1. Calculate BMI
2. Calcuate EAR for protein
Explain how carbon monoxide reduces the carrying capacity of red blood cells.
What are the consequences of high blood pressure?
What are the consequences of low blood pressure?
Give examples for when EAR for protein may vary;
What is the difference between first and second class protein?
Describe how the following are stored;
1. Carboydrates
2. Fats
3. Proteins
For the following write the pathogen that causes the disease;
1. Athletes foot
2. Flu
3. Cholera
4. Malaria
Name 4 ways that the body is defended from pathogens;
What is the difference between passive and active immunity?
With reference to malaria:
1. The host is;
2. The parasite is;
3. The vector;
Give two ways that white blood cells help fight disease:
Describe changes in lifestyle that reduce the risk of some cancers.
Explain how pathogens cause the symptoms of an infectious disease.
What is the difference between monocular and binocular vision?
What is the cause of the following;
1. Short sight
2. Long sight
3. Colour blindness
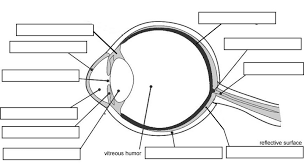
Label the eye.
Outline the process of immunisation.
What is the difference between benign and malignant
Explain why a double blind trial might be used to test new drugs (HSW)
Explain the need for careful use of antibiotics
Describe what happens at a synapse
How are motor neurones adapted to their function?
Explain how the eye focuses light
Describe the path of the reflex arc
What is the CNS?
What are sensory neurones?
What are relay neurones?
What effect does depressants have on you?
Example?
What effect does stimulants have on you?
Example?
What drug category blocks nerve impulses?
What are performance enhancers?
E.g??
What drug category distorts what is seen or heard?
Whats the effects of the following things that are in cigarettes;
1. Nicotine
2. Tar
3. Carbon monoxide
4. Particulates
Give 4 short term effects of alcohol.
Give 2 long term effects of alcohol.
Why is there a legal limit for alcohol for drivers and pilots?
What is the cause of 'smokers cough'?
Explain the basis of the legal classification system for drugs (A-C)
What is the normal body temperature?
What is homeostasis?
List 3 things that the body needs to keep constant;
How could you control type 2 diabetes?
How could you control type 1 diabetes?
What are the effects on the body if temperature is too high?
What are the effects on the body if temperature is too low?
Explain why responses controlled by hormones are usually slower than responses controlled by the nervus system.
Explain how vasodilation and vasoconstriction increase or reduce heat transfer to the environment
Describe how the liver can be damaged as it removes alcohol.
Describe how the action of depressants and stimulants differ on the nervous system.
Explain how negative feedback mechanisms help to maintain a constant internal environment.
Growing towards light is called ............ phototropism. And away from gravity is called negative ..........................
Growing towards gravity is called .................
Give 4 commercial uses of plant hormones.
Plant hormones are called ..................
- Move through the plant in .........
- Involved in the response to i...........
- Involved in the response to g.................
Describe an experiment to prove that plants grow towards light.
LIst characteristics that are as a result of both genes and environment
How many chromosomes are thre in a skin cell?
How many chromosones in an egg cell?
How many chromosones in a sperm cell?
What are the sex chromosomes for a girl?
What are the sex chromosomes for a boy?
List 3 causes of variation.
Name 4 inherited disorders
Explain how auxin brings about shoot curvature in terms of cell elongation.
Define homozygous.
Define heterozygous
Whats genotype?
What phenotype?
Define dominant.
Define recessive.
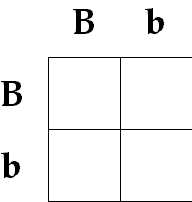
Complete the monohybrid cross
Define allele.

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes