FLASHCARDS - Heterogeneous Catalysis
Pineado a
17
0
0
Sin etiquetas
|
|
Creado por Sulivan González
hace más de 8 años
|
|
Cerrar
|
|
Creado por Sulivan González
hace más de 8 años
|
|

Benefits of Heterogeneous Catalysts (3 P)
Surface area formula
IUPAC definition... size for:
1) Micropores
2) Mesopores
3) Macropores
Variable surface chemistry
2D Materials:
- Clays
Clays - neutral, no catalyst activity
--> Isomorphous substitution: inserts charge into system: more active catalyst
Clays:
- Effect of isomorphous substituion
Clays:
- Effect of isomorphous substituion 2
Catalyst activation
Pillaring cations
Layer collpase - problem especially w/ high charge density cations
Reactions of clays
Other layered materials
3D Catalysts
- Microporous systems
Catalytic sites within zeolites
Acidic Zeolites
Pore size and diffusion
Pore size and diffusion 2: (3 P)
Diffusion in porous materials depend on: (3 P)
5 stages involved in a liquid phase reaction using a porous solid catalyst
- NOTE: for gas phase reactions, thickness of hydrodynamic layer = 0, so 1) and 5) can be omitted
5 stages involved in a liquid phase reaction using a porous solid catalyst 2
- Optimizing performance:
Test for diffusion control
How is pore size measured (2 P):
How is pore size measured
- Porosimetry
Measuring acidity of zeolites
Shape selectivity - Key property of zeolites (eg H-ZSM5)
Reactant selectivity
Other uses of zeolites
Titanium silicates (TS-1): Oxidation catalyst
Titanium silicates (TS-1): Oxidation catalyst 2
Titanium silicates (TS-1) w/ 2 Ti: Oxidation catalyst
Mesoporous systems - Larger templates give unstable materials.
Solution...
Addition of Heteroatoms to MTS
ALMA industrial process
Catalyst =
\((VO)_2P_2O_7\)
What is meant by isomorphous substitution in context of porous solids

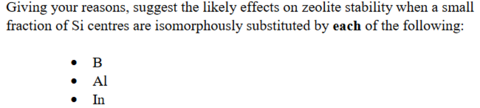

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes