Cerrar

Simple Molecules
Covalently bonded substances fall into two main types:
1.Simple molecules
2.Giant covalent structures
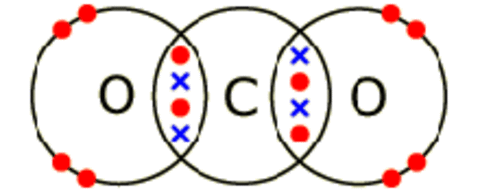
Low melting and boiling points - This is because the weak intermolecular forces break down easily.
Hydrogen, ammonia, methane and water are also simple molecules with covalent bonds. All have very strong bonds between the atoms, but much weaker forces holding the molecules together. When one of these substances melts or boils, it is these weak 'intermolecular forces' that break, not the strong covalent bonds. Simple molecular substances are gases, liquids or solids with low melting and boiling points.
Macromolecules have giant covalent structures. They contain a lot of non-metal atoms, each joined to adjacent atoms by covalent bonds.
Substances with giant covalent structures have very high melting points, because a lot of strong covalent bonds must be broken e.g. Graphite.
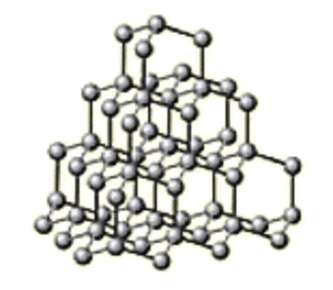
Diamond is a form of carbon in which each carbon atom is joined to four other carbon atoms, forming a giant covalent structure.
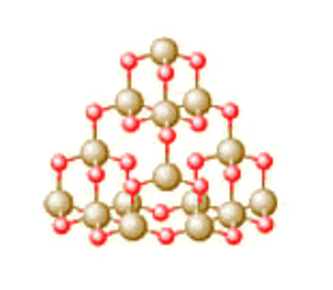
Graphite is a form of carbon in which the carbon atoms form layers.
It is used in pencils and as a lubricant. Graphite conducts electricity.
Silica
A polymer is a large molecule formed by many identical smaller molecules (monomers).
Thermosoftening polymers
Poly(ethene) is a thermosoftening polymer. Its tangled polymer chains can uncoil and slide past each other, making it a flexible material.
Thermosetting polymers
Vulcanised rubber is a thermoset used to make tyres. Its polymer chains are joined together by cross-links, so they cannot slide past each other easily.
Ionic compounds
Ionic bonds are the electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions.
Their melting and boiling points are very high because ionic bonds are very strong so a lot of energy is needed to break them.
However, ionic compounds do not conduct electricity when they are solid. This is because their ions cannot move around in their lattice structure.
Metals are malleable (they can be bent and shaped). This is because they consist of layers of atoms. These layers can slide over one another when the metal is bent, hammered or pressed.
Metals form giant structures in which electrons in the outer shells of the metal atoms are free to move. These are called 'delocalised electrons'

Alloys
Alloys contain atoms of different sizes. These different sizes distort the regular arrangements of atoms. This makes it more difficult for the layers to slide over each other, so alloys are harder than the pure metal.
Fullerenes
Fullerenes may be used for drug delivery systems in the body, in lubricants and as catalysts.

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes