Cerrar

What type of heat transfer occurs in solids?
What type of heat transfer occurs in fluids (liquids and gases)?
What is Infra-Red Radiation?
What is conduction?
What is convection?
How is conduction stopped?
How is convection stopped?
How is infra-red radiation stopped?
What does infra-red radiation happen in?
Which surfaces best emit radiation?
Which surfaces best reflect radiation?
Is air a good, or poor conductor?
How does double glazing stop conduction?
How does cavity wall insulation stop conduction and convection?
What does a vacuum do in terms of heat transfer?
What is Specific Heat Capacity (SHC)?
What does a low specific heat capacity mean for a material?
What is Specific Latent Heat?
What unit is heat measured in?
What is heat?
How is temperature measured?
What is temperature?
On heating graphs, what do flat areas of constant temperature show?
Describe heat flow.
Describe what happens in ovens.
Describe what happens in microwave ovens.
What are thermograms?
Name the parts of a transverse wave:
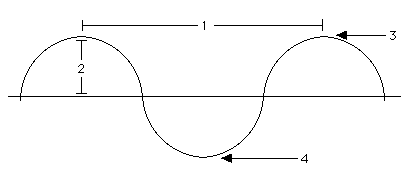
What does frequency mean?
What is the electromagnetic spectrum going from:
High frequency/low wavelength
TO
Low frequency/high wavelenth
What are the uses of Gamma waves?
What are the uses of X-rays?
What are the uses of Ultraviolet?
What are the uses of visible waves?
What are the uses of infra-red?
What are the uses of microwaves?
What are the uses of radio waves?
What is total internal reflection (TIR)?
How do optical fibers use TIR?
What is the connection between frequency and energy in waves?
What is the connection between darker skin and UV rays?
Is a higher or lower factor sun cream better for protection against UV rays?
What does the factor on sun cream mean?
What is the connection between UV rays and the Ozone Layer?
What is an analogue signal? Describe its shape.
What is a digital signal? Describe its shape.
What are the advantages of digital signals?
What is Morse Code?
How do lasers read CDs?
How does wireless technology work?
What is the ionosphere?
What happens in microwave communication?
How do microwaves lose signal strength?
In microwave communication, what happens to signals of similar frequencies?
What happens in Radio Communication?
In radio communication, what happens to signals of similar frequencies?
What are seismic waves?
How many types of seismic waves are there?
What are the two types of seismic (shock) waves?
Describe P waves.
Describe S waves.
What happens when a substance is heated?
What is an absolute scale?
Why is energy measured on an absolute scale?
What happens if there is a difference in temperature between two places?
The greater the difference in temperature, what will happen to the rate of cooling?
Do materials which need to gain lots of energy to warm release:
a) lots of energy
b) little energy
What happens in boiling?
What happens in melting?
What happens in condensing and freezing?
What is condensing?
When does convection occur?
How do immersion heaters work?
Why can't convection happen in solids?
What method of heat transfers do radiators use?
How do we get heat from the Sun?
How is heat radiated?
How is radiation different from conduction and convection?
What is the connection between heat and amount of radiation emitted?
Does everything emit and absorb heat radiation?
What happens to cooler objects with heat radiation?
What happens to matt black surfaces with heat radiation?
What happens to light-coloured, smooth and shiny objects with heat radiation?
Which surfaces are poor emitters and absorbers of radiation?
Which surfaces are very good absorbers and emitters of radiation?
How do grills and toasters work?
Why do people line their grill pan with shiny foil?
What are microwaves?
Why don't you cover microwave food with foil? What is better?
What is another term for wasted?
What are things that emit energy called?
What are things that transfer/waste/lose energy called?
What does insulation do?
How does insulation both cost AND save you money?
What is payback time?
What is loft insulation?
What is it's average payback time?
What does a hot water tank jacket do?
What is its average payback time?
What is draught-proofing?
What is its average payback time?
How do thick curtains save energy?
What are their average payback time?
What is its average payback time for cavity walls & insulation?
What is a cavity wall?
What does double glazing stop?
What is its average payback time?
How are thermograms taken?
How do thermograms work?
Why are machines useful?
What happens to energy that is inputted into a machine?
What is the link between energy wastage and efficiency?
What is the symbol for wavelength?
What do Sankey diagrams do?
What is a similarity between light and heat waves?
What is the amplitude of a wave?
What is the frequency on a wave?
What is frequency measured in?
What is a wavelength?
1kHZ (kilohertz) is equivalent to how many Hz?
1MHZ (1 megahertz) is equivalent to how many Hz?
How do waves travel?
What happens when waves arrive at an obstacle?
How do we see things?
What is the law of reflection?
What happens when light reflects off an uneven surface?
What happens when light reflects off an even (smooth and shiny) surface?
What does TIR stand for?
What is TIR dependent on?
In reflection...
What happens if the angle of incidence is LESS than the critical angle?
In reflection...
What happens if the angle of incidence is EQUAL to the critical angle?
In reflection...
What happens if the angle of incidence is GREATER than the critical angle?
When they pass through a gap or pass an object, what do all waves do?
What is the amount of diffraction dependent on?
In relation to wavelength...
How would a narrow gap be described?
If a gap is much wider than the wavelength, how much diffraction will occur?
If a gap is a bit than the wavelength, how much diffraction will occur?
If a gap is the same size as the wavelength, how much diffraction will occur?
Describe the wavelengths of light.
Can it be diffracted?

 Ocultar las fichas que te sabes
Ocultar las fichas que te sabes