AQA Alevel psychology approaches in detail
|
|
Created by Ellie Porter
over 7 years ago
|
|

Approaches in Psychology
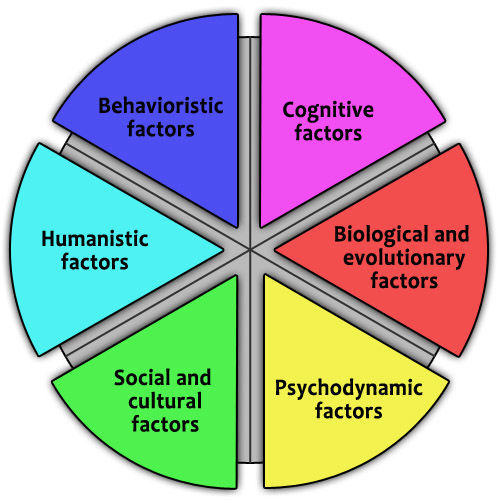
Order of Approaches

Wilhelm Wundt - Introspection
1879
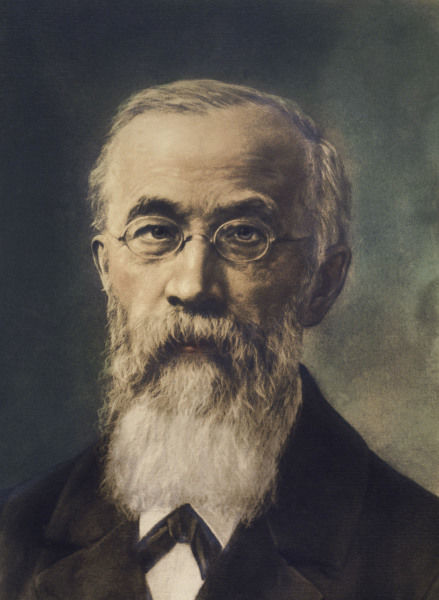
Sigmund Freud - Psychodynamic Approach
1900's

Id: Unconscious thought - selfish and aggressive instincts which demand immediate gratification
Ego: Reality check - balancing demands of the Id and Superego
Superego: Moralistic part of personality which represents the ideal self of who we ought to be
Strengths -
Theory had a large influence on early psychology & western thought
Can be practically applied through psychoanalysis
Watson & Skinner - Behaviourist Approach
1913

Studies behaviour that can be observed & measured
Basic processes are the same in all species
Strengths -
Scientifically credible as observations are in highly controlled lab settings and helps for replication
Principles have been applied to real life situations such as token economies
Albert Bandura - Social Learning Theory

Behaviour is learned through observation and imitation as well as direct and indirect conditioning
Strengths -
A more comprehensive account of learning
Helps explain cultural differences
Less deterministic than behaviourism
Cognitive Approach
1960's
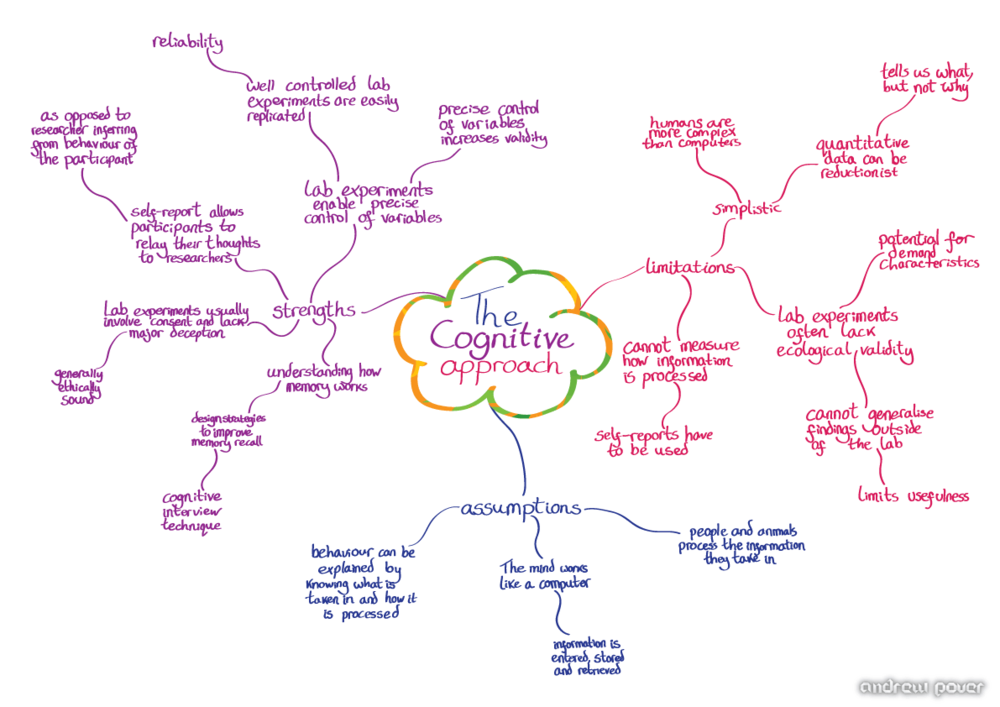
Internal mental processes should be studied scientifically and inferences on what is happening should be made indirectly
The mind is like a computer
Strengths -
Lab experiments produce reliable & objective data
Has influenced development of artificial intelligence and machines like robots
Less deterministic than other approaches

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards
