
Blood Components
Blood's Function
Composition of Blood
55% :
45% :
1-2%:
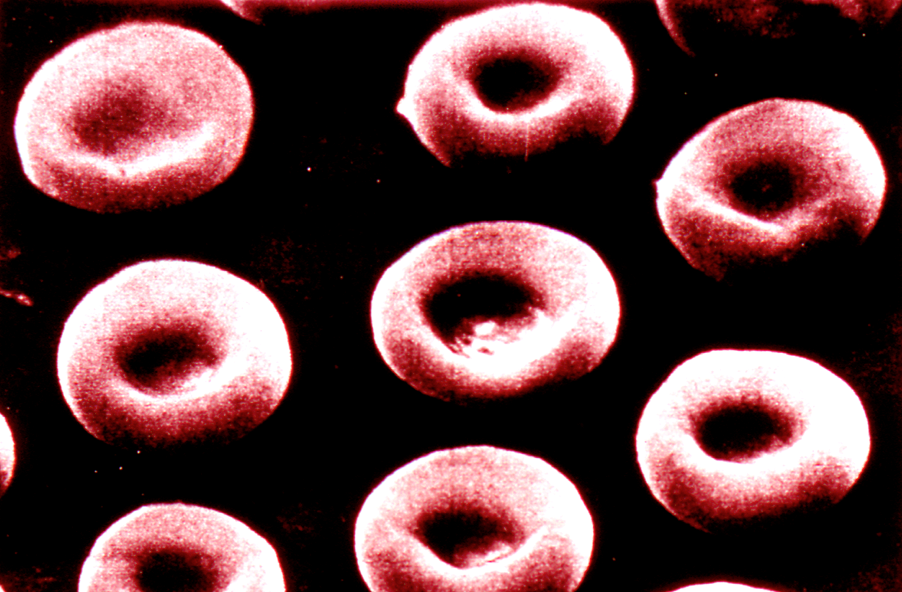
Scanning E.M. of Erythrocytes
Making a BLOOD SMEAR
-Drawing it out is to dilute the cells (some WBC's may burst from this)
Properties of RBC's
(small specs in image are platelets: look like cellular debris)
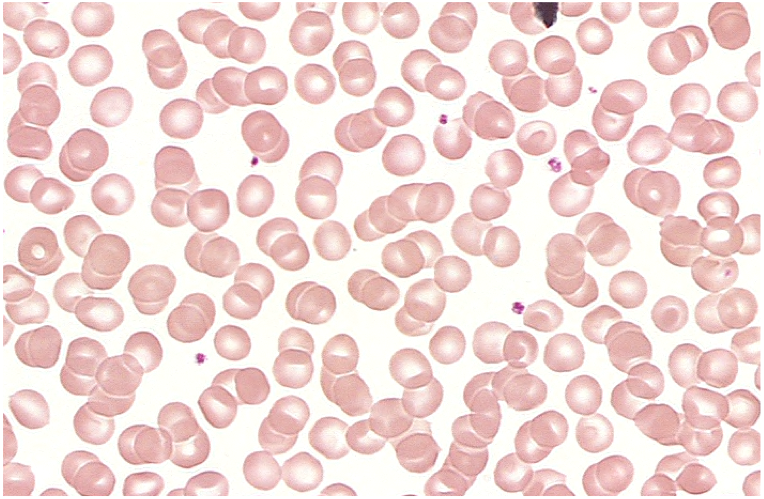
Erythrocyte Function
Thalassemia
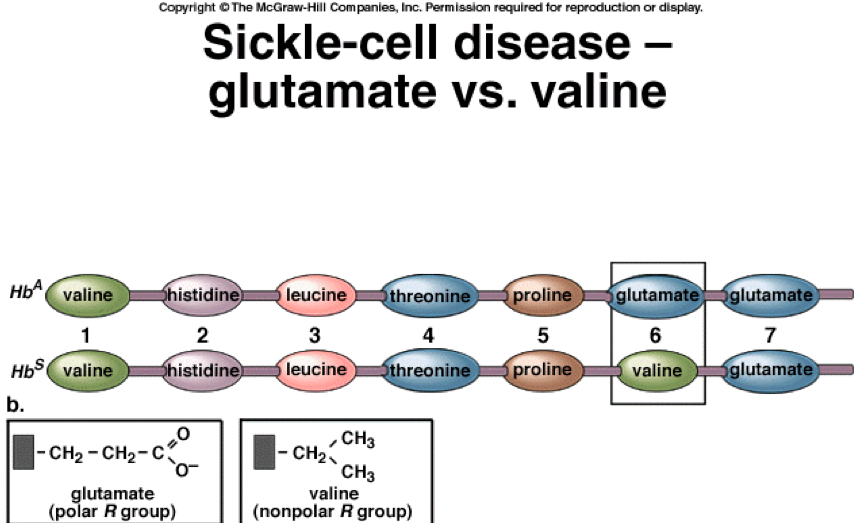
Sickle Cell
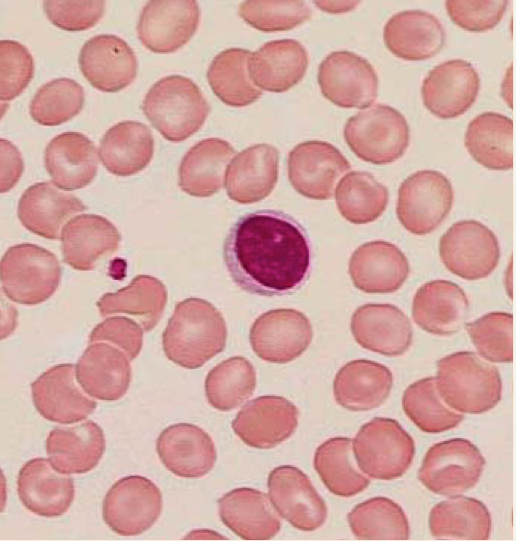
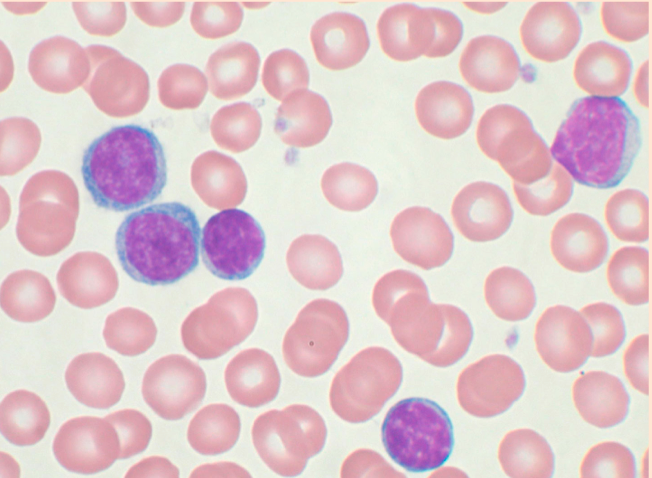
Peripheral Blood Leukocytes
Lymphocytes
(agranulocyte)
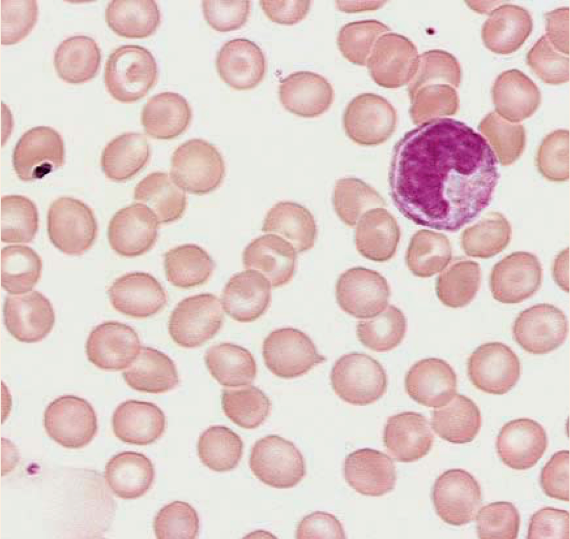
Monocytes
(agranulocyte)
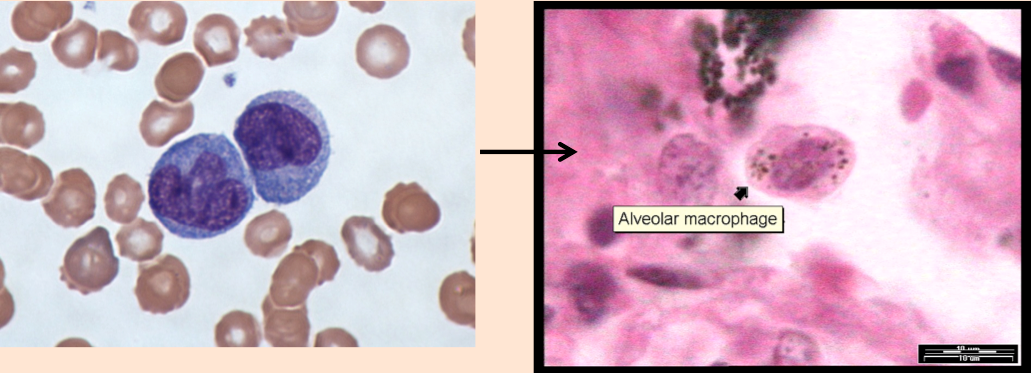
Macrophages
(derived from monocytes)
Neutrophils
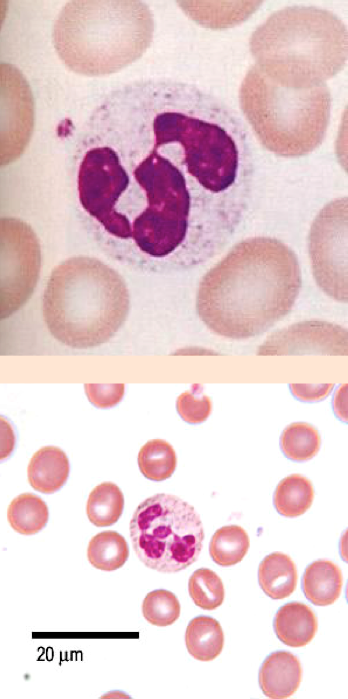
Neutrophils are the FIRST responders to inflammatory sites!
Neutrophils ATTACK
Propionibacterium acnes
(bacteria in hair follicle + PMNs = PIMPLE)
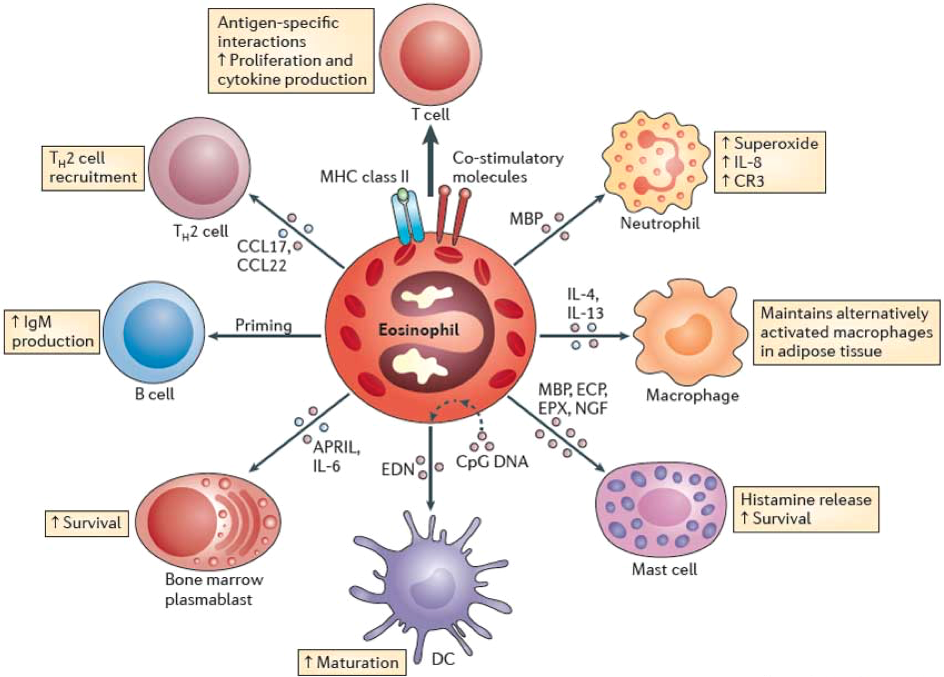
Eosinophils
**Granules are same color as surround RBC's
ATTACK Parasites
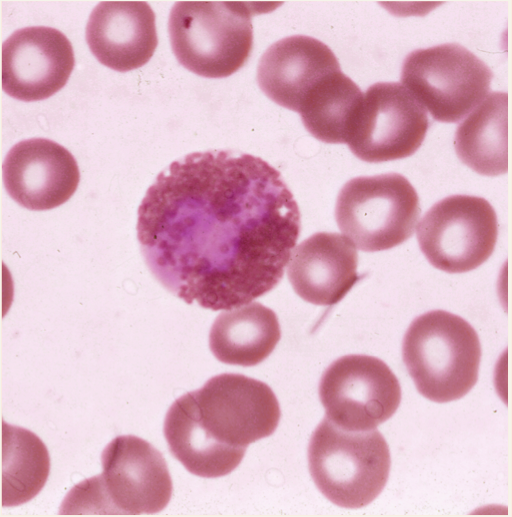
Eosinophils have MANY functions but main ones involved with are:
Basophils
**BLUE/purple granules
bi-lobed, bluish nucleus
act like mast cells to mediate inflammatory process
Ectoparasites!
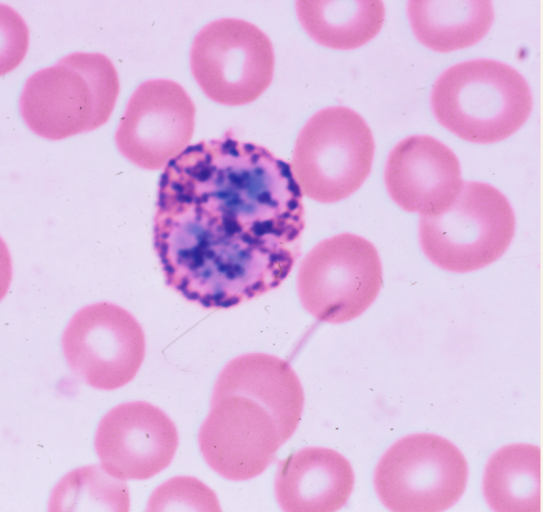
Basophils MAIN function:
Platelets
(look like cellular debris)
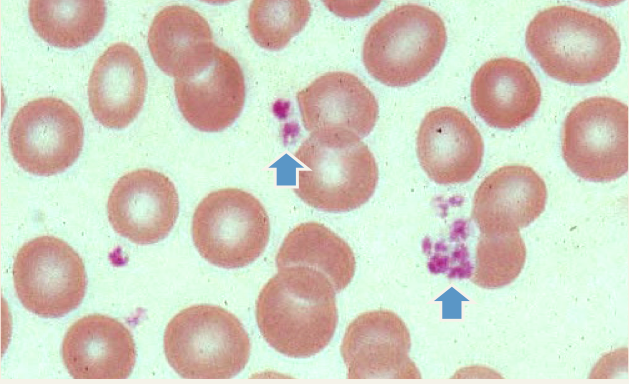
Platelets main function =
BLOOD CLOTTING
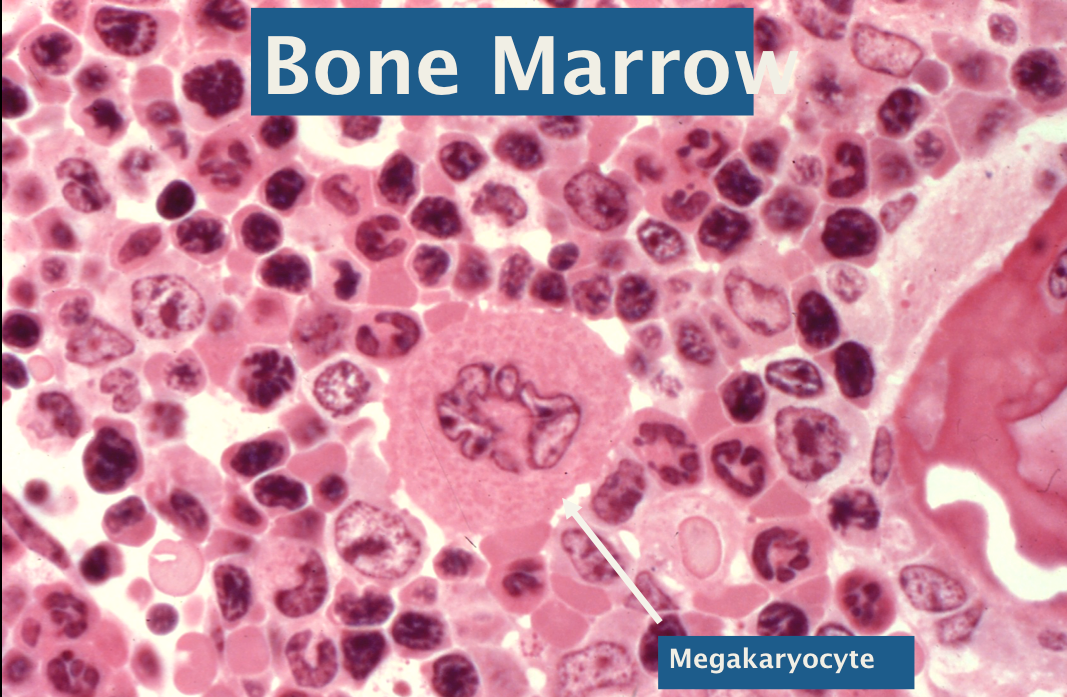
Megakaryocytes
(in bone marrow)
Exam Question
The white blood cells in this smear:
A. Can clot blood
B. Rush to site of infection to phagocytose bacteria
C. Can leave blood and differentiate into plasma cells
D. Activate with parasite infection

 Hide known cards
Hide known cards
