Year 10 AQA Revision cards - Blood
Pin adicionado em
195
0
0
|
|
Criado por Lily Eaves
mais de 6 anos atrás
|
|
Fechar
|
|
Criado por Lily Eaves
mais de 6 anos atrás
|
|

The composition of the blood:
55% plasma
45% red blood cells
>1% white blood cells
Haemaglobin is a large protein molecule folded around four iron ions
Oxygen + Haemaglobin = Oxyhaemaglobin
Red blood cells:
carry oxygen to the lungs for aerobic respiration
are in the shapes of biconcave discs for increased surface area to volume area for diffusion
the pigment that red blood cells contain is haemaglobin
White blood cells:
the role of this cell is to defend the body from harmful microorganisms
the lymphocytes from antibodies against microorganisms
antitoxins act against poisons from microorganisms
Platelets:
are small cell fragments
they clot the blood at wounds
during the blood clotting process, there is a series of enzyme-controlled reactions that result in converting fibrinogen to fibrin
protects the new skin as it grows
Plasma:
90% of plasma is water
it transports blood cells and dissolved substances around the body
the urea is formed in the liver from a breakdown of excess protein carried to the liver by plasma and disposed as urine
Blood vessels:
there are three main blood vessels capillaries, arteries and veins
Veins have thin walls which mean they have larger lumen, they contain blood under low pressure and often have valves to stop the blood from flowing backwards
A double circulatory system is one transport system from the heart to the lungs and back and one that transports blood the heart to the organs and back
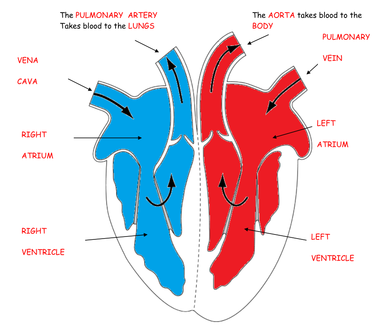
The left ventricle wall is thicker than the right ventricle wall because it needs to push the blood further into the systemic circuit (body) compared to the pulmonary circuit (lungs)
the pulmonary vein. The blood enters the heart at the left atrium and then travels to the left ventricle. The heart contracts, forcing the blood out of the heart into the aorta, which transports the blood to the rest of the body
An artificial pacemaker is an electrical device that has a wire, that is commonly placed within a vein, to send electrical impulses to the heart
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD):
risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity and inactivity
Bypass surgery uses general anaesthetic and is a more risky treatment for CHD. Doctors use sections of blood vessels from other blood vessels in the body to replace the blocked area. This is only used when an artery is too blocked for stents to be effective. This can be expensive.
Leaky valves:
Mechanical valves- Durable and longlasting but the patient needs to take medication for the rest of their life
Biological valves- don't damage red blood cells but only lasts around 12-15 year

 Ocultar acertos
Ocultar acertos