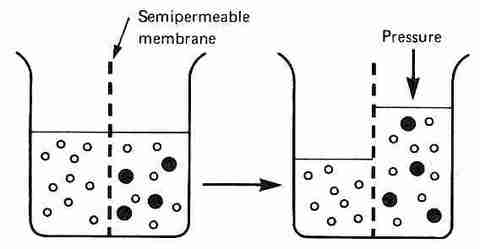
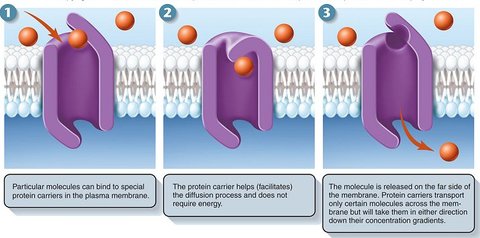
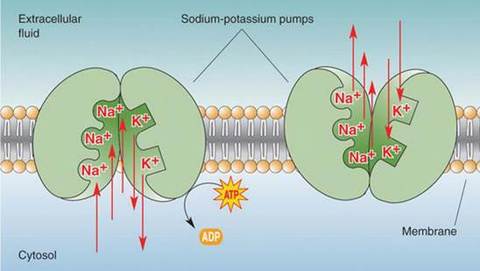
Anatomy and Physiology FlashCards sobre Transport accross a cell membrane, criado por Kirsty Lesniak em 21-09-2013.
Pin adicionado em
742
2
0
Sem etiquetas
|
|
Criado por Kirsty Lesniak
aproximadamente 11 anos atrás
|
|
Fechar