FlashCards sobre PNB 2265 Practical 1, criado por Nicole Servetnik em 23-02-2022.
Pin adicionado em
38
1
0
Sem etiquetas
|
|
Criado por Nicole Servetnik
quase 3 anos atrás
|
|
Fechar
|
|
Criado por Nicole Servetnik
quase 3 anos atrás
|
|

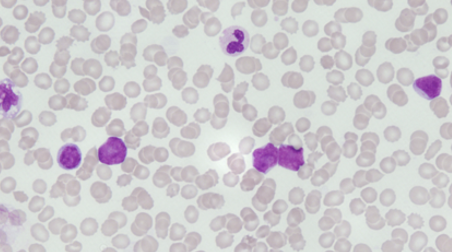
this is the most abundant type of blood cell
these are biconcave cells that deliver oxygen to tissues, are very numerous
these cell fragments do not have a nucleus and help to form blood clots (small purple crescents between RBCs)
these cells are separated into granulocytes and agranulocytes
these white blood cells contain many dark staining granules in the cytoplasm and the nucleus typically takes on a multi-lobed appearance
these white blood cells contain very few dark staining granules in the cytoplasm
these 3 white blood cell types are granulocytes
these 2 white blood cell types are agranulocytes
this white blood cell releases chemicals that change blood pressure. look for dense staining of granules in cytoplasm that obscure nucleus.
this white blood cell responds to the site of an acute injury or infection and performs phagocytosis of debris. look for a nucleus of 3-4 dark staining lobes with many dark staining granules in the cytoplasm.
this white blood cell responds to allergens and chronic inflammation. they release chemicals that change blood pressure. look for nuclei with two lobes and many dark staining granules in the cytoplasm.
what is the order of white blood cells in order of most to least abundant
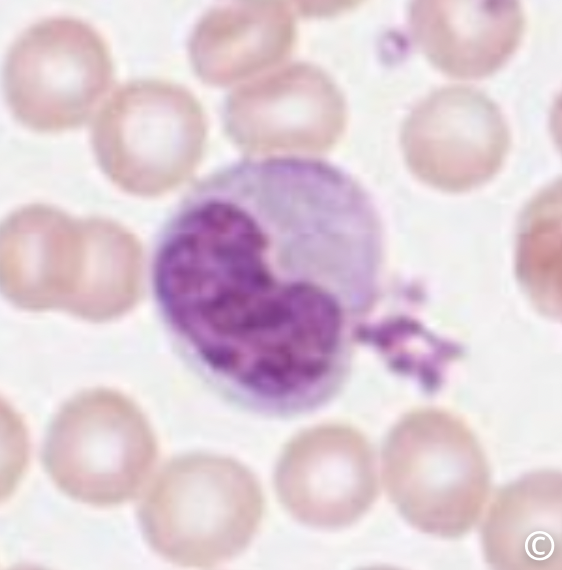
what is this cell
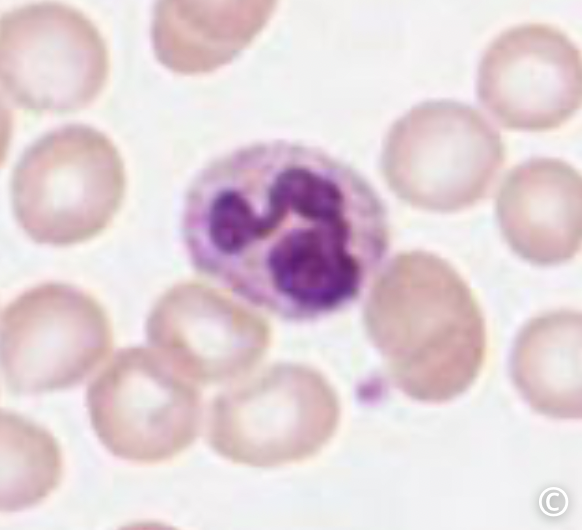
what is this cell
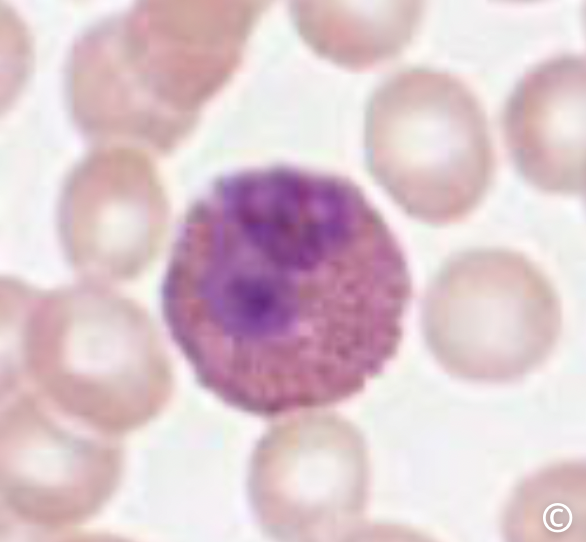
what is this cell
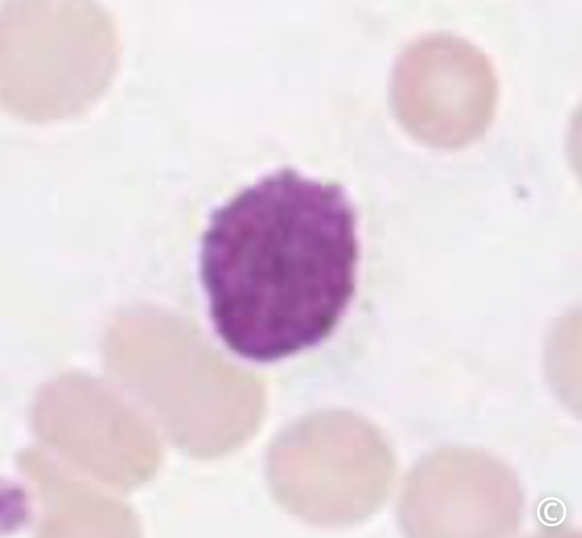
what is this cell
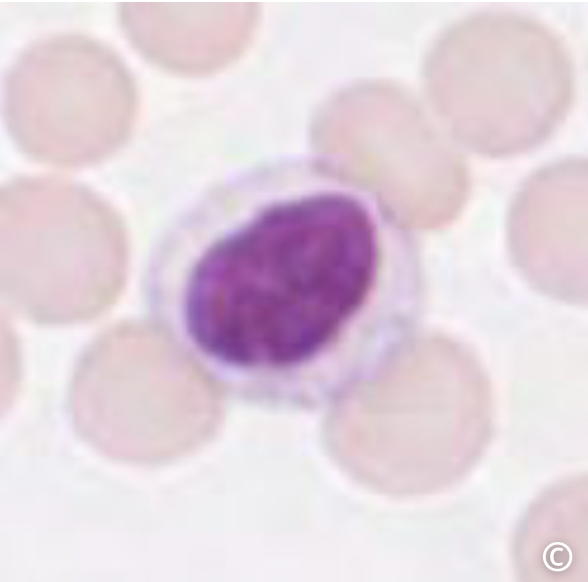
what is this cell
what is this blood disease
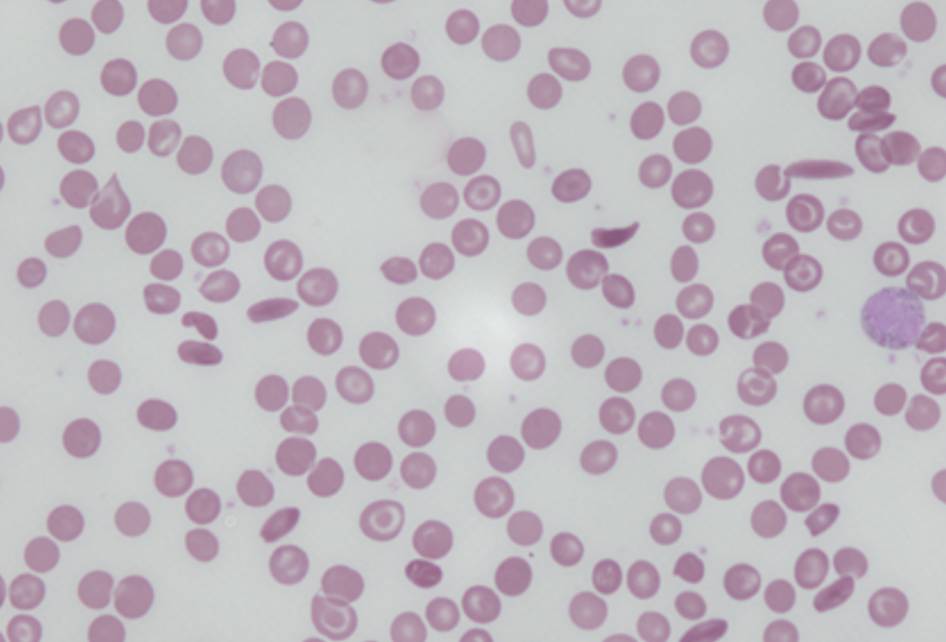
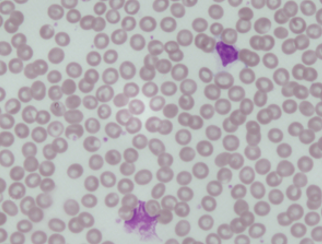
what is this blood disease
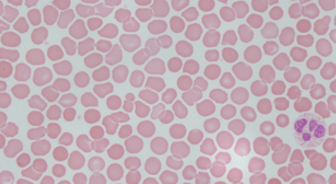
this is a viral blood disease caused by the Epstein-barr virus which results in an increased production of monocytes and lymphocytes (agranulocytes)
what is this blood disease
this is the abnormal increase in the number of erythrocytes which increases viscosity of blood. often a result of bone marrow cancer.
what is this blood disease
this type of cancer involved an overproduction of leukocytes. cells and immature/abnormal in appearance and lack normal function. can be acute or chronic.
this is the main component of RBCs and has four folded proteins called globins. the red pigment is called heme
hemoglobin is important because each one of these molecules binds an oxygen
typical range of hemoglobin for a male
type range of hemoglobin for a female
the Hb-O2 curve is this shape
this is a diagnostic test to see the portion of RBC's in a blood sample
in a completed hematocrit, the upper clear yellow layer is ___, the Buffy coat is ___, and the lower dark red layer is ____.
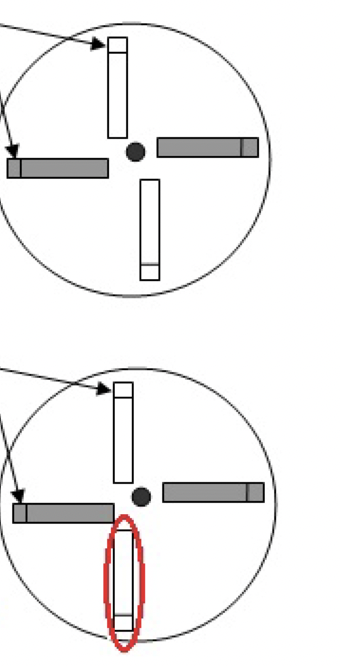
what is the proper way to balance centrifuge tubes? top or bottom picture?
what is the calculation for hematocrit packed red blood cell volume?
the hematocrit is (higher/lower) than normal if a patient has anemia
the hematocrit is (higher/lower) than normal is a patient has polycythemia
the hematocrit is (higher/lower) than normal if a patient has compensated blood loss
the hematocrit is (higher/lower) than normal is a patient is suffering with dehydration
the hematocrit is (higher/lower) than normal is a patient is blood doping
what happens to the hematocrit when you have leukemia
this is determined by which antigen is present on a person's blood cells
Blood type A has these antibodies and can receive blood from ___ and donate blood to ___.
Blood type B has these antibodies and can receive blood from ___ and donate blood to ___.
blood type AB has these antibodies and can receive blood from ___ and donate blood to ___.
blood type O has these antibodies and can receive blood from ___ and donate blood to ___.
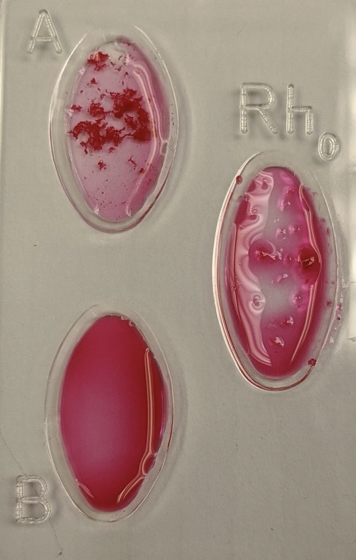
what is this blood type?
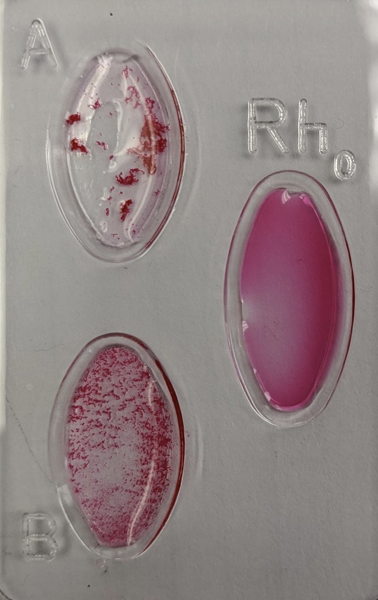
what is this blood type?
when you plot the amount of oxyhemoglobin vs oxygen concentration you obtain a
hemoglobin exhibits this kind of binding
what is p50?
this shift to the Hb-O2 curve means p50 is higher, oxygen affinity is lower, there is more CO2, less H+, higher DPG, or higher temperature
this shift to the Hb-O2 curve means p50 is lower, oxygen affinity is higher, there is less CO2, more H+, lower DPG, or colder temperature
this was used to monitor the proportion of oxyhemoglobin present in the sample
what wavelength do you use on the spectrophotometer for hemoglobin?
this is the wavelength where the substance shows max absorbance
this plot shows the intensity of color related to the amount of substance present
Calculation for saturation of hemoglobin
For the saturation of hemoglobin, what did A, B and C stand for in the saturation equation?
this is the pressure at which half of hemes are bound to oxygen
what is beers law and what does each component stand for
which has higher oxygen affinity? myoglobin or hemoglobin?
which has higher oxygen affinity? fetal hemoglobin or adult hemoglobin?
the positive electrode for ECG is placed on the
the negative electrode for ECG is placed on the
the earth electrode for ECG is placed on the
what structure is labeled 1
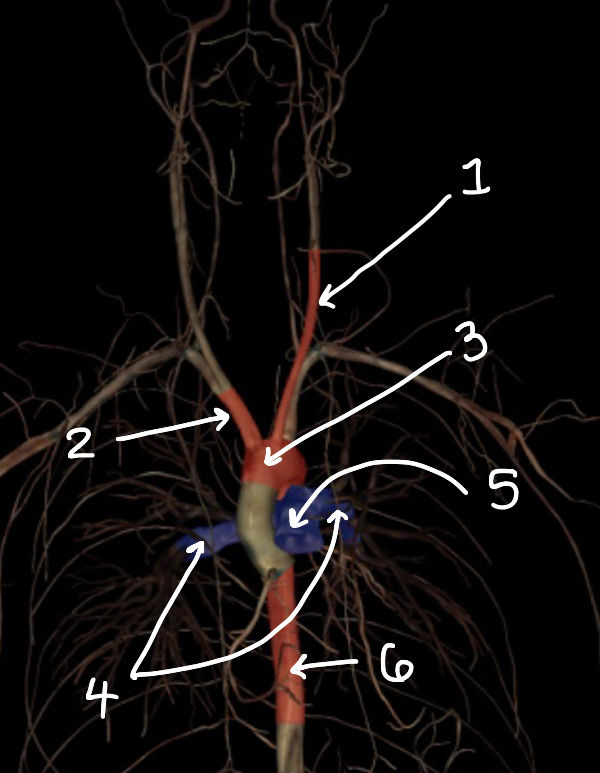
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 5

what structure is labeled 6

what structure is labeled 1
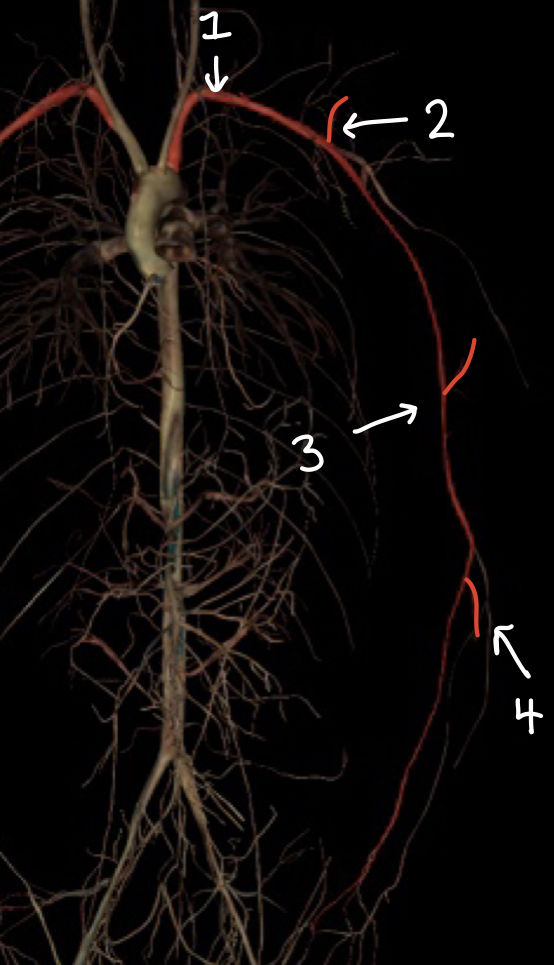
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 1
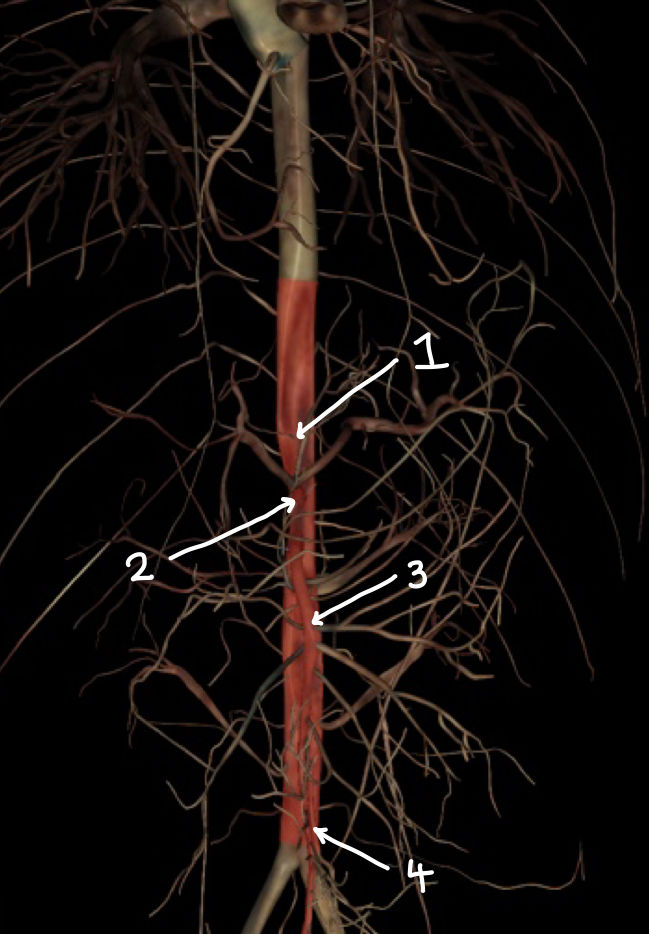
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 1
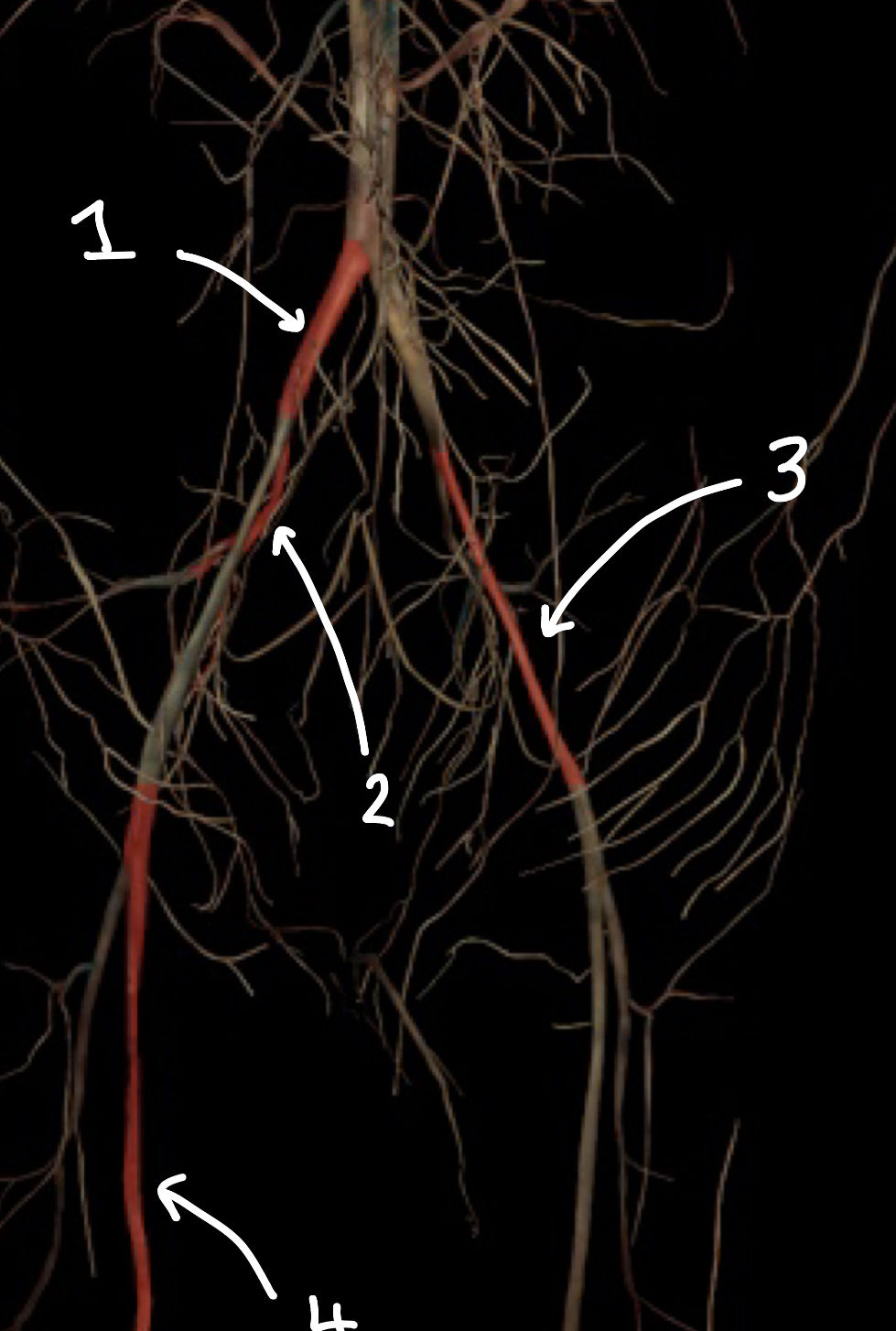
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 1
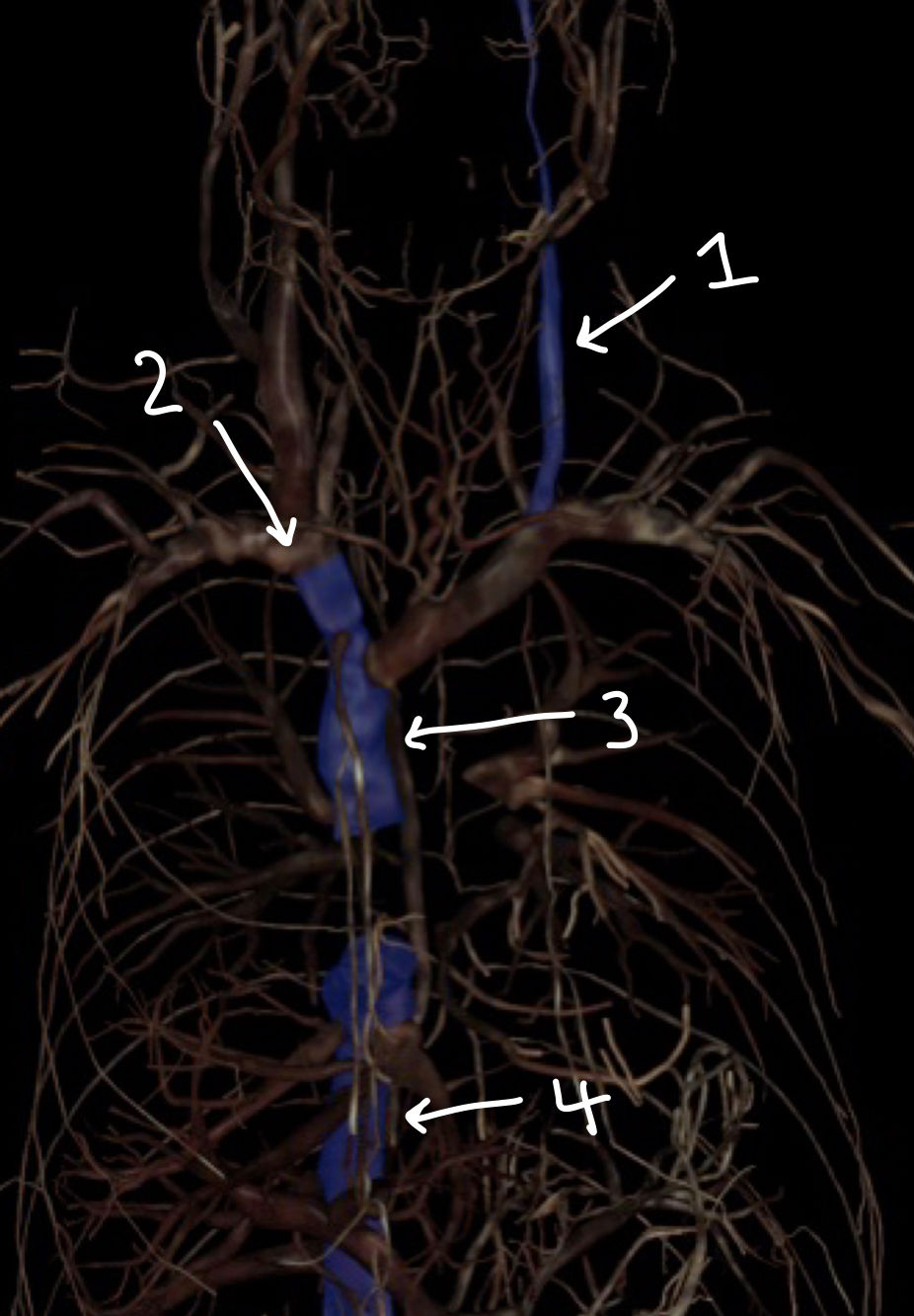
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 1
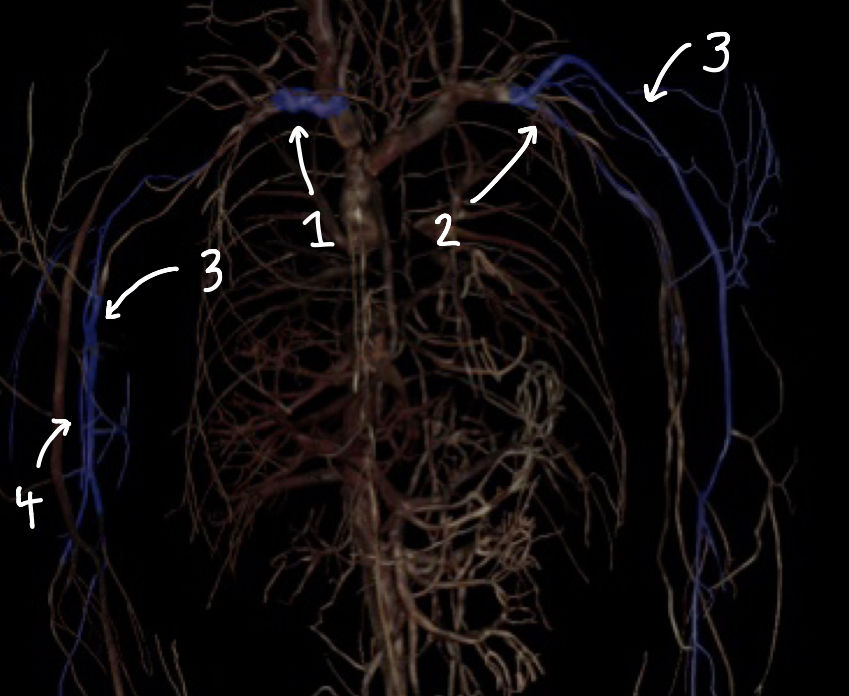
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 1
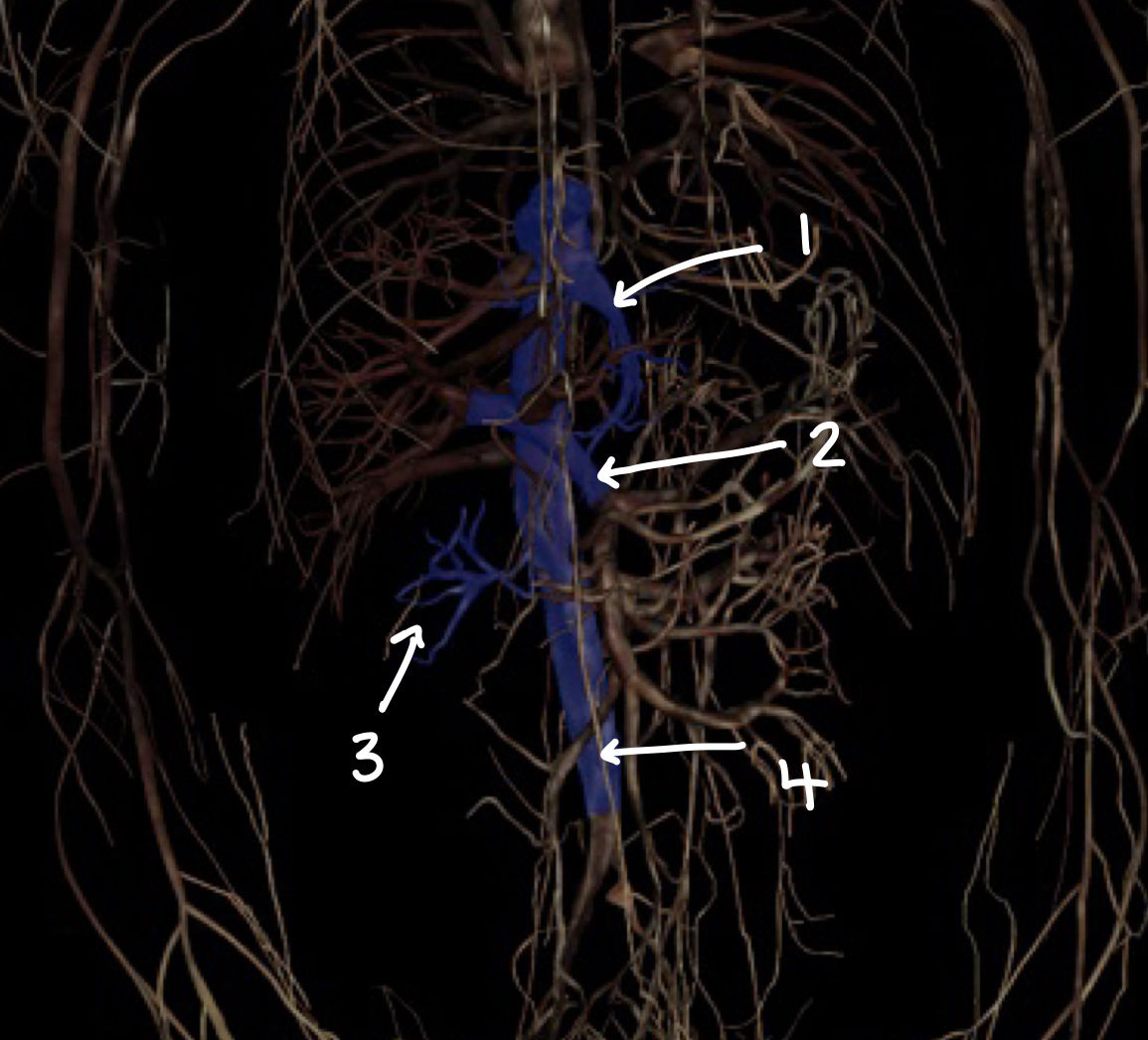
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 1
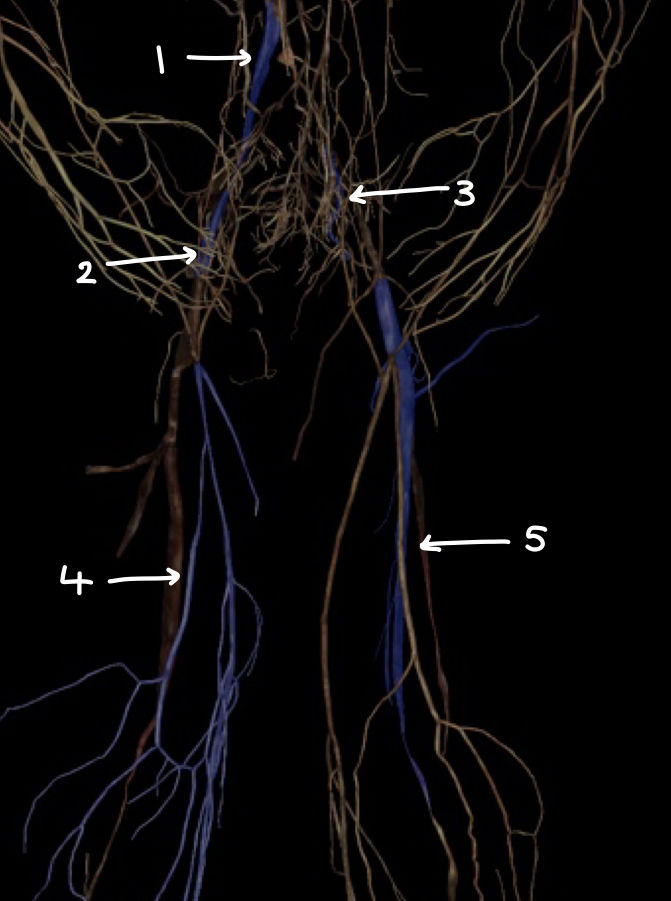
what structure is labeled 2

what structure is labeled 3

what structure is labeled 4

what structure is labeled 5

what is A
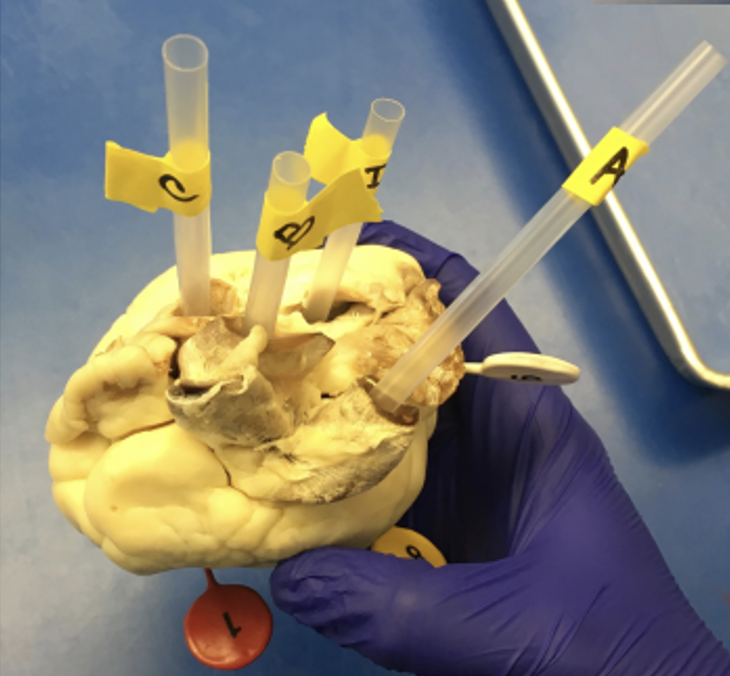
what is B

what is C

what is D

what is 2
what is 3

what is 4

what is 5

what is 6

what is 7

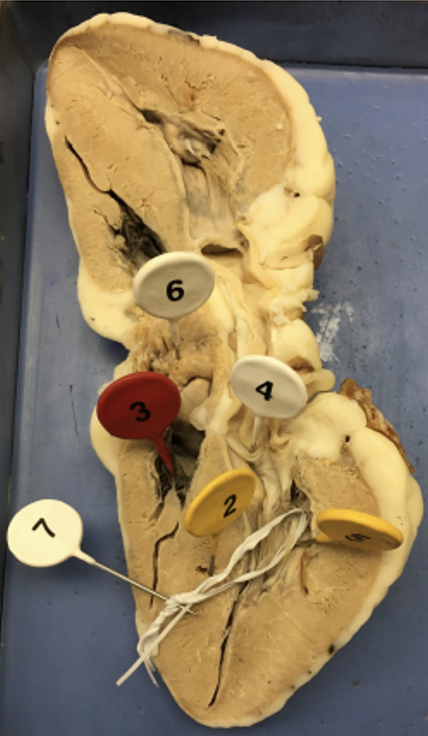
what is 1
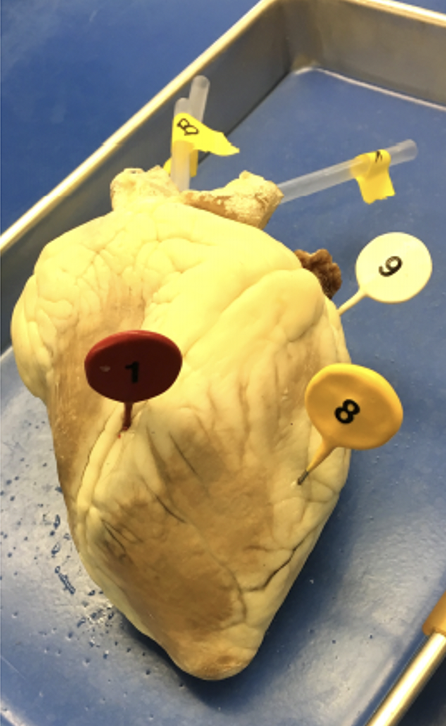
what is 8

what is 9

what is 1
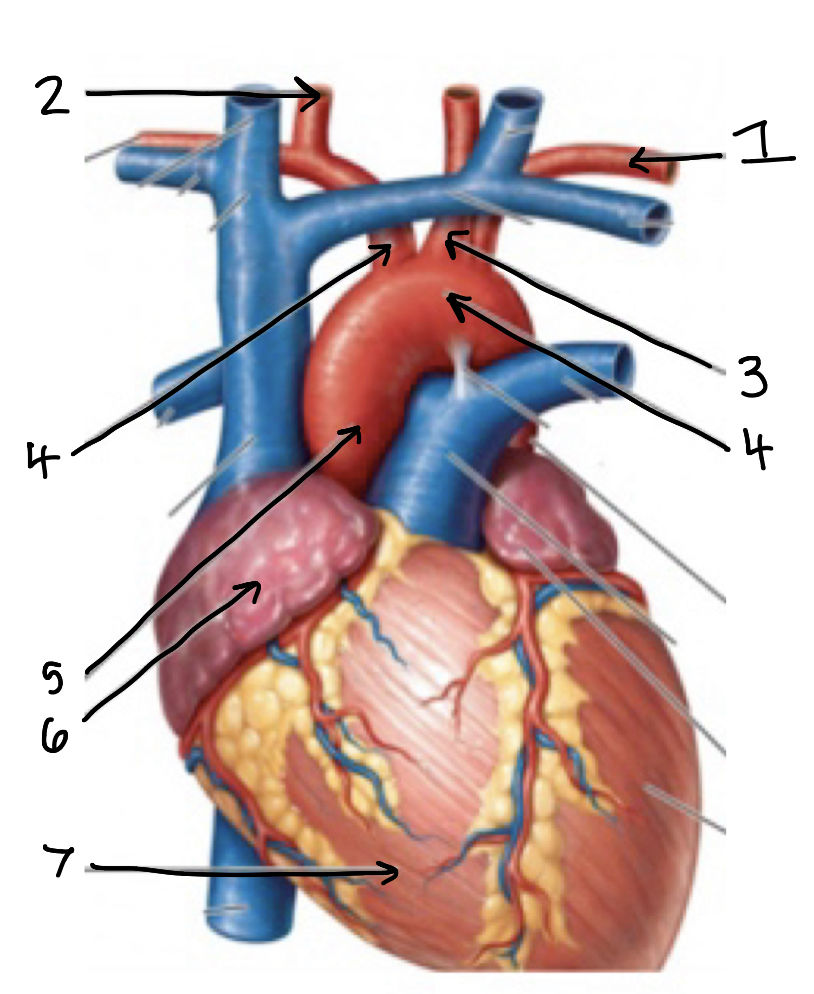
what is 2

what is 4 on the left side (anatomical position)

what is 4 on the right side (anatomical position)

what is 5

what is 6

what is 7

arteries carry blood (away from/to) the heart
veins carry blood (away from/to) the heart
the size of the lumen is bigger on an artery or a vein
the thickness of the wall is larger on an artery or a vein
what is 1 and 2
the lub sound (first heart sound) is created because these valves close
the dub sound (second heart sound) is created because these valves close
in this wave of the ecg, there is atrial depolarization
in this wave of the ecg, there is atrial repolarization and ventricular depolarization
in this wave of the ecg, there is ventricular repolarization
how is p wave amplitude and duration affected after exercise
how is qrs amplitude and duration affected after exercise
how is the t wave amplitude and duration affected after exercise
when does the first heart sound happen based on an ecg
when does the second heart sound happen based on ecg
what is the calibration force for the force transducer setup
the positive lead attaches to this part for the frog experiment
the negative lead attaches to this part for the frog experiment
the earth lead attaches to this part for the frog experiment
how many atria and ventricles do frogs have compared to humans
is there oxygen separation in the frog heart
where are the pacemaker cells in a frog compared to human
a decrease in temperature results in this change in heart rate. this is because proteins and enzymes require higher temperatures to work efficiently.
an increase in calcium concentrations leads to these changes in force and HR. the reasoning is that calcium facilitates the cross bridge formation between thick and thin filaments which increases contractility.
an increase is potassium concentration leads to this change in HR and force. this is because potassium depolarizes the membrane potential of pacemaker cells and decreases driving force.
when adding isuprel to the frog heart, this is how HR and contractile force changed. This is because it activates beta1 adrenergic receptors which causes Gs stimulation, increases adenyl cyclase, increase cAMP, increase HCN channel activity, increase pKa, increase calcium concentration.
when adding Ach to a frog heart, this happens to HR. This is because Ach activates muscarinic receptors and causes Gi stimulation which decreases adenyl cyclase, cAMP, HCN channel activity, decrease pKa, decrease calcium concentration.
When adding atropine then Ach to the frog heart, this is what happens to HR and force. This is because atropine is a plant alkaloid that blocks muscarinic receptors.
When mechanically stretching the frog heart, this is the expected observation. This is because of the frank-starling law
absolute refractory in a frog heart causes this channel to inactivate
in frog heart experiment, which peak represents atrial contraction and ventricular contraction (big peak of little peak)
what are the primary lymphoid organs
what are the secondary lymphoid organs
this lymphoid organ is bi-lobed,
Capsule- connective tissue
Cortex- T cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, epithelial cells
Medulla- more mature T cells, macrophages, dendritic cells, Hassall’s corpuscles
this region is the darker region of thymus due to presence of lymphocytes, in comparison to this region, which has less dense concentration
this lymphoid organ filters blood and is the site of initiation of immune response
this pulp in the spleen serves as site of storage of RBCs and filters them
this pulp in the spleen contains clusters of T cells, B cells and Macrophages
what is the difference between indirect and direct ELISA?
this lymphocyte doesn't involve antibodies, matures in the thymus, and directly kills infected host cells
this lymphocyte secretes antibodies, matures in the thymus and bone marrow, and provides defense against pathogens

 Ocultar acertos
Ocultar acertos