Fechar

1. Biological Psychologists
2. Neurons
3. Sensory (afferent) neurons
4. Motor Neurons (efferent)
5. Interneurons
6. Mirror Neurons
7. Soma (cell body)
8. Axon
9. Axon Terminals
10. Dendrites
11. Myelin Sheath
12. Action Potential
13. "All or none principle"
14. Resting Potential
15. Threshold
16. Synapse (synaptic gap)
17. Neurotransmitters
18. Excitatory Neurotransmitters
19. Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
20. Reuptake
21. Acetylcholine (Ach)
22. Dopamine
23. Serotonin
24. Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)
25. Endorphins
26. Central Nervous System
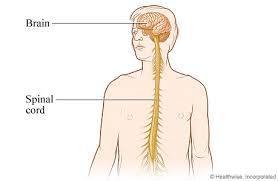
27. Peripheral Nervous System
28. Sympathetic Nervous System
29. Parasympathetic Nervous System
30. Reflexes
31. Endocrine System
32. Hormones
33. Adrenal Glands
34. Pituitary Gland
35. Lesion
36. Electroencephalogram (EEG)

37. Computed Tomography (CT) scan
38. Positron emission tomography (PET) scan
39. Magnetic resonance imaging
40. f MRI (functional MRI)
41. Hindbrain
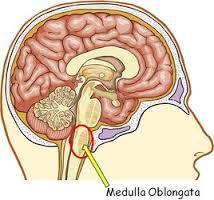
42. Medulla
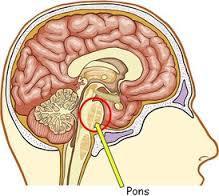
43. pons
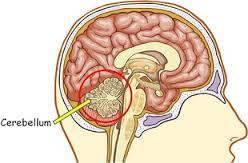
44. Cerebellum
45. Midbrain
46. Reticular formation
47. Forebrain
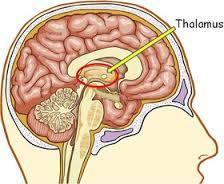
48. Thalamus
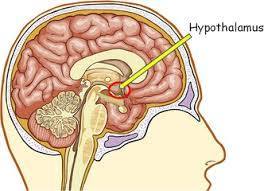
49. Hypothalamus
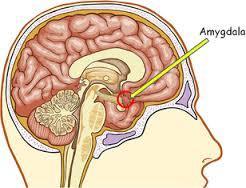
50. Amygdala
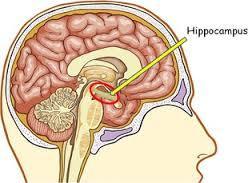
51. Hippocampus
52. Limbic System
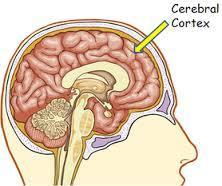
53. Cerebral Cortex
54. Left Hemisphere
55. Right Hemisphere
56. Brain Lateralization
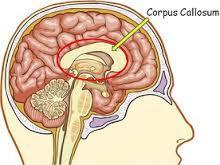
57. Corpus Callosum
58. Lobes
59. Association Areas
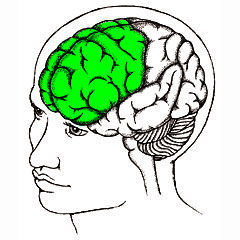
60. Frontal Lobe
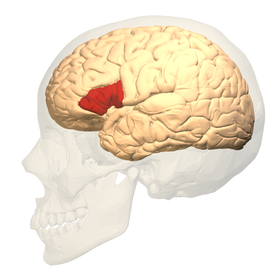
61. Broca's Area
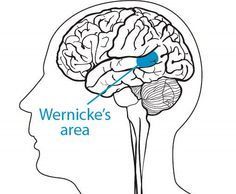
62. Wernicke's Area
63. Aphasia
64. Motor Cortex
65. Sensory Cortex
66. Parietal Lobe
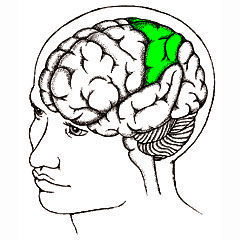
67. Occipital Lobe
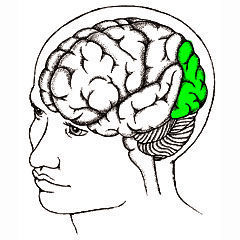
68. Temporal Lobe
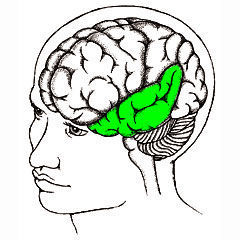
69. Brain Plasticity
70. Roger Sperry
71. Prosopagnosia
72. Parkinson's Disease
73. Schizophrenia
74. Multiple Sclerosis
75. Alzheimer's Disease

 Ocultar acertos
Ocultar acertos