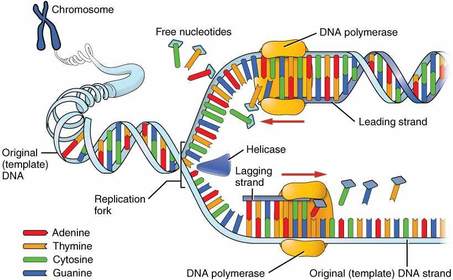
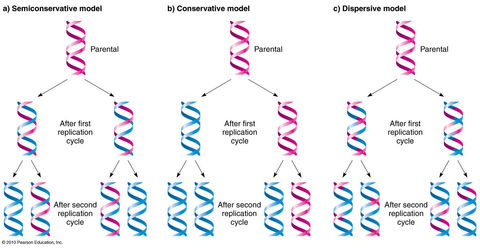
AS - Level Biology (Nucleic acids and their functions) FlashCards sobre DNA replication, criado por Emily Sutton em 25-02-2016.
Pin adicionado em
121
3
0
Sem etiquetas

|
Criado por Emily Sutton
quase 9 anos atrás
|
|
Fechar