Fechar

Describe the term efficiency

Explain the condition needed for something to keep at a constant temperature
Explain how an electric current is induced by a magnet and wire
Describe Galileo's observations and explain how they changed our ideas of the universe

Recall the life cycle of a star the similar in mass to our sun
Recall the life cycle of a star with a greater mass then our sun
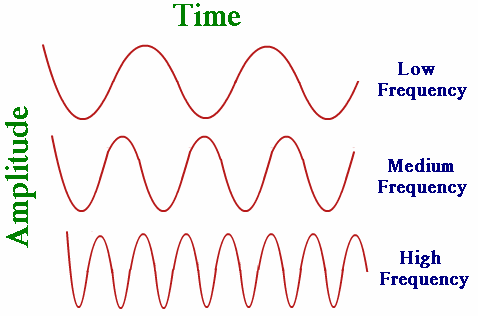
Describe how potential danger is related to the frequency of a wave
Explain how to measure the focal length of a lens
Describe what happens to all waves at a boundary between different materials
Recall what ionising radiations are emitted by
Describe the term redshift
Describe the terms current and voltage
Describe what all waves do and do not transfer
Describe the dangers of microwave, infra-red and ultraviolet radiation
State the people discovered IR and UV and describe their experiment
Recall the shared properties of all EM waves
Explain why waves refract at a boundary between different materials
State the evidence that supports the big bang theory
Explain why some telescopes are located outside the earths atmosphere
Describe the three advantages of modern telescopes
Explain how a main sequence star is formed from a nebula
State what causes the motion of tectonic plates
Describe the terms ultrasound and infrasound
Explain why step-up transformers are used in the transmission of electricity
Describe how to calculate payback times
List the waves of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing frequency/decreasing wavelength
Explain why the Big Bang theory is more accepted then the steady state theory
Describe law of conservation of energy
Explain how data from seismometers can be used to identify the location of an earthquake
Explain how earthquakes are caused at plate boundaries
Describe the term Power and state its units
State how scientists use waves to find out information about our Universe
Define the term amplitude
Define the term wavelength
Define the term frequency
Describe the differences between longitudinal and transverse waves
Identify sound, electromagnetic and seismic waves as transverse or longitudinal.
State the order of the visible spectrum
Describe some uses of radiowaves
Describe some uses of microwaves
Describe some uses of infrared
Describe some uses of visible light
Describe some uses of ultraviolet
Describe some uses of x-rays
Describe some uses of gamma rays
State ionising radiation from the nucleus of an atom
State the name of the galaxy that the Solar System is part of
Define a galaxy
Define the Universe
Describe the methods used to gather evidence for life beyond Earth
Explain what is meant by the CMBR (cosmic microwave background radiation)
Explain why the red-shift of galaxies provides evidence for the Universe expanding
Describe some uses of ultrasound
Describe uses of infrasound
State two ways that seismic waves are generated
Explain why scientists find it difficult to predict earthquakes and tsunami waves even with available data.
Describe the factors that affect the size of an induced current
State the main forms of energy

 Ocultar acertos
Ocultar acertos