Respiratory System
Pin adicionado em
25
0
0
Sem etiquetas
|
|
Criado por Amelia Claire
mais de 8 anos atrás
|
|
Fechar
|
|
Criado por Amelia Claire
mais de 8 anos atrás
|
|

Primary Functions of Respiratory System
Conducting Portion of Respiratory System
Respiratory Portion of the
Respiratory System
Functions of the Nose
Pharynx / Throat
Respiratory Epithelium
irritants cause hyper production of mucus
Lung Lobes
Trachea anterior to oesophagus
trachea extends to:
bronchial tree
Primary Bronchus
Secondary Bronchi
Bronchioles
Parasympathetic system impact on Bronchioles
Sympathetic Nervous System and Adrenaline's impact on bronchioles
Parasympathetic Nervous System affect on ARTERIOLES
Sympathetic and Adrenaline impact on ARTERIOLES
bronchioles are sensitive to local chemicals
Bronchioles are dynamic
bronchopulmonary lobule
terminal bronchiole subdivides;
Alveolar Type 1 Cells (predominant)
Alveolar type 2 Cells (interspersed)
Alveolar Macrophages (move around)
Gas Exchange
Diffusion Barrier
Fick's Law of Diffusion
R inverse to A ΔP / d
or R = D(constant)A ΔP/d
diffusion =
blood supply to respiratory surface
Pleural Membranes / Pleural Sac
parietal pleura
visceral pleura
3 processes of respiration
Pulmonary Ventilation (breathing)
external respiration
Pulmonary Ventilation
Boyle's Law
Pressure differentials created by changes in lung volume
Inhalation
Exhalation
Muscles involved in deep breathing
Intrapleural Pressure
tranpulmonary pressure gradient
intraplueral fluid
Factors Affecting Pulmonary Ventilation
Factors Affecting Pulmonary Ventilation:
Lung Compliance
Factors Affecting Pulmonary Ventilation:
Elastance
Factors Affecting Pulmonary Ventilation:
surface tension of alveolar fluid
Airway Resistance
Factors Affecting Pulmonary Ventilation:
Pathology - COPD, Emphysema, chronic bronchitis
Cause by inflammatory response by lung;
obstructive diseases
Restrictive Diseases
Lung Volume
vital capacity
Alveolar Ventilation
(takes part in gas exchange)
gas exchange
Fick's Law
Dalton's Law
henry's law
composition of air
pulmonary gas exchange
gas exchange
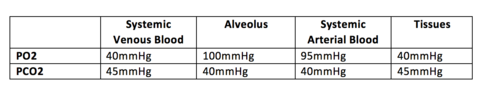
transport of oxygen

 Ocultar acertos
Ocultar acertos