Semester 1: Lecture 1 Study Notes.
Pin adicionado em
127
0
0
Sem etiquetas
|
|
Criado por Sam Barnes
aproximadamente 8 anos atrás
|
|
Fechar
|
|
Criado por Sam Barnes
aproximadamente 8 anos atrás
|
|

What is the fuselage?
What defines a Truss Type Fuselage?
What are the five stresses on airframe?
What is a Flutter?
What defines the Monocoque Fuselage?
What defines a Semi-Monocoque?
What is a composite?
What are the five advantages of Composites?
What are two disadvantages of Composites ?
Name Wing attach points and wing dihedrals.

What is the Ground-Loop Phenomenon?
Name the entire tail group (consisting of fixed and movable surfaces)
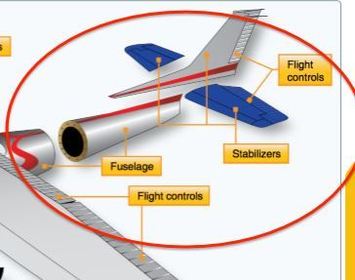
What parts make up the Empennage?
(Part 1)
List all parts of the Empennage
(part 2)
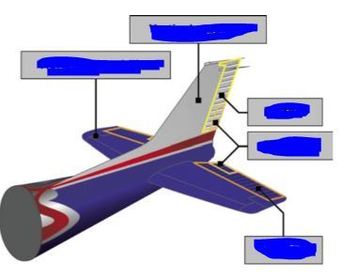
What parts make up "Flight Controls?"
Name all the control surfaces
What are the three main categories of aircraft engines?
What are the three airplane movements?
What control surface is responsible for a Roll?
What control surface is responsible for a Pitch move
What control surface is responsible for a Yaw move
If struggling to understand this movement watch the following video ...
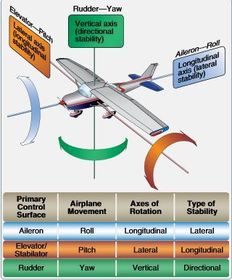
Name the three Axes of rotation (three angles perpendicular (90 degrees) from one another)
A Roll (Aileron) is on which axis of rotation?
A Pitch (Elevator/Stabilator) is on which axis?
A Yaw (Rudder) is on which axis?
Name this undercarriage landing gear configuration.

Name this undercarriage landing gear configuration.

What is the function of the landing gear?
What are three reasons for why the tri-cycle landing gear is better than the tail-dragger?
What are the two types of Flight Controls?
(Optional) Primary flight controls consist of ...
(Optional) Auxiliary flight controls consist of ...
Name this part of the aircraft
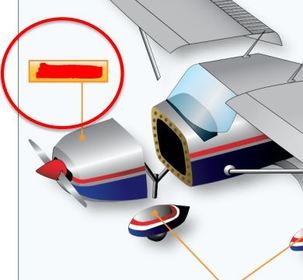
Name the three basic components of the Powerplant.
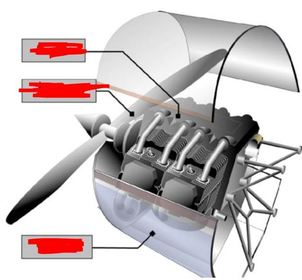
Slide 2 ~ Powerplant
List all of the Turbo-prop engine components.
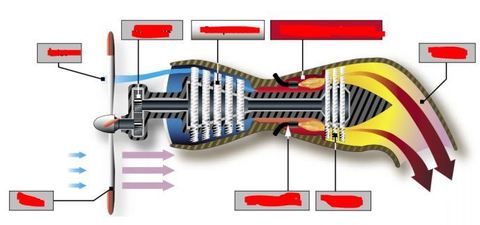
What is the oxford definition of a Reciprocating Engine?
Basic Physic's Process - how does the engine create power?
List the five types of reciprocating engines.
Name the Reciprocating Engine Type:
A smaller frontal area and is better adapted to streamlining but proper cooling is difficult with increase in engine size
Name the Reciprocating Engine Type:
Two in-line banks generally set 60° apart
Name the Reciprocating Engine Type:
A row, or rows, of cylinders arranged radially about a central crankcase.
Main advantage is the favourable power-to-weight ratio
Name the Reciprocating Engine Type:
Most popular type used on smaller aircraft.
Main advantages include: high power-to-weight ratio and reduction in drag.
List the two primary designs for reciprocating engine (ignition).
What is a Four-stroke engine and how many pistons doesn't it require for a full cycle?

What are the 4 PROS of a Four-stroke engine design?
What are the two CONS of a Four-stroke engine design?
What is a Two-stroke engine and how many pistons doesn't it require for a full cycle?
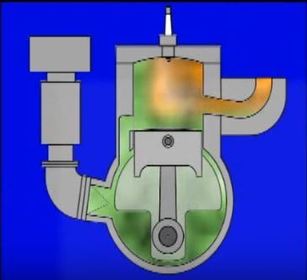
What are the 3 PROS of a TWO-stroke engine design?
What are the 2 CONS of a two-stroke engine design?
List all power-plant components labelled in this diagram

What role do Cylinders play within a powerplant?
What role do Piston play within a powerplant?
What role do Connecting rod play within a powerplant?
What role do Crankshaft play within a powerplant?
What role do Camshaft play within a powerplay?
What role do Pushrod play within a powerplant?
What role do Valves play within a powerplant?
In order, list the four processes in a four-stroke cycle.
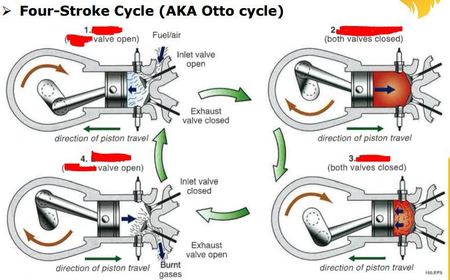
How does the valve & piston behave for INTAKE?
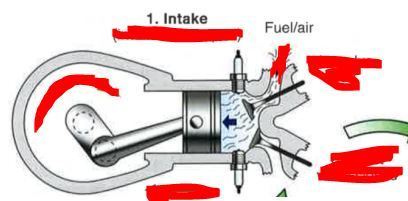
How does the valve & piston behave for Compression?
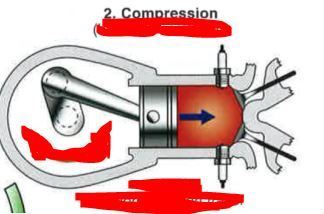
How does the valve & piston behave for Power?
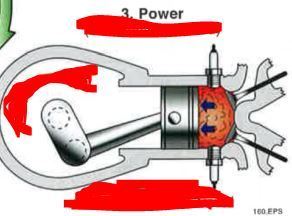
How does the valve & piston behave for Exhaust?
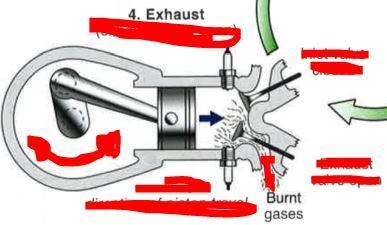
Revise Question:
In order, list the four steps to a Four-stroke cycle?
What is Carburation?
What is the purpose of the carburation system.

 Ocultar acertos
Ocultar acertos