Fechar

Did you know that revision cards have something written on their back?
Proton and Neutron contribute to relative atomic mass by 1
Electrons do not.
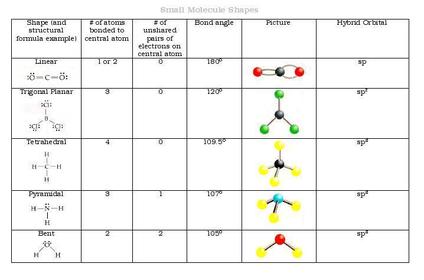
Dot-and-cross diagrams
displayed formulae
structure formulae
each atom has its own Mr (mass number) and atomic (proton number)
how would you find number of electrons?
TOF Mass Spec.
(time of flight mass spectrometer)
is a straight tube
TOF mass spec produces ions with +1 charge only.
TOF mass spec.
produces a graph with relative abundance on y axis and M/Z on x axis
(mass to charge (charge = +1) ratio)
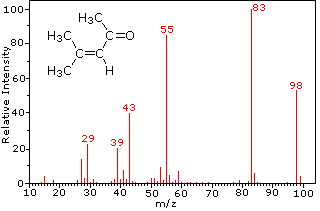
TOF mass spec can be used to determine the Mr. but you'll have to combine all the isotope numbers first.
The average atomic mass of an element is the sum of the masses of its isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance.
Source: Boundless.
You'll be asked to give
'full electron configuration' of an element
1s2------------------------------>
2s2------------------------->2p6
3s2------------------------->3p6
4s2--------->3d10-------->4p6
Periodic table is split into 4 groups of sub-levels: S, P, d, F
each can handle 2,6,10,14 electrons respectively
You won't be asked about f block
When finding electron configuration
d block does something weird
4s2 is followed by 3d10, not 4d10
why?
(this is the only period of such nature I've seen asked at exams, dont get caught out)
Initial Ionisation energy - energy required to remove outermost electron
[x] ---> [x+] + e-
You will be asked to complete a box diagram for electron configuration of a subshell level. we use half arrows pointing up and down to represent electrons in the same density spinning in opposite ways.
boxes are filled by single electrons, until they have to pair up.
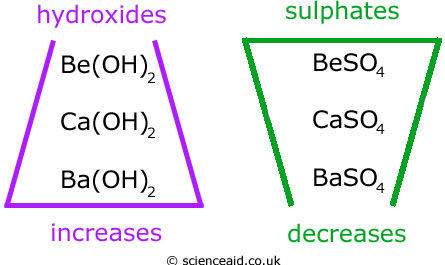
Group 2 solubility
Relative Molecular Mass (Mr)
Mr = mass of one Mole of (molecule) relative to 1/12 of one Mole of Carbon 12
Carbon mass 12
Oxygen mass 16
Hydrogen mass 1
Mol
grams/Mr = Mol = Conc. x Vol.(dm3)
1 mol of Carbon12 is 12 grams exactly
Avogadro's constant
how many of these are in a Mol?
H atoms?
H2O molecules ?
Tomato Pizzas?
Ideal Gas Equation
PV=nRT
pressure(bar) x volume(Litres) = Mol x Constant(8.22) x temperature(Kelvin)
you'll be asked to "find x"
Empirical formulae
- simplest whole number ratio of atoms -
In the old days, people had a list of atoms and their ratios to work with. this was used to find the actual molecular formulae
Find Empirical formulae of:
C6O6H12
by mass C 83.33% H 16.67%
Using mass percentage/ratio to get empirical formula.
by mass C 83.33% H 16.67%
divide by individual's Mr
C 6.94 H 16.67
divide by the smallest (6.94)
C 1 H 2.4
Multiply both by a number such to get whole number ratio. (x5 in this case)
C 5 H 12
Ionic Equations
split (aq) aqueous solutions into ions.
common ones:
KOH---> K+ OH-
NaI----> Na+ I-
Write equations out
CH3CH2CH3 for propane instead of C3H8
You'll do titration of acid into base or base into acid
Acid is H+
Base is OH-
water can dissociate to form these
Atom economy (by mass)
(mass of needed product)/(mass of reactants) x 100
same as "percentage of" calculation
Ionic Bonding
(a potentially infinite lattice)
electrostatic attractions
between anions and cations
Metallic Bonding
(a potentially infinite lattice)
Attraction between Cation (metal) like Fe+ and the shared sea of delocalised electrons
Macromolecular
(giant covalent)
(a potentially infinite lattice)
attraction to shared pair of electrons
Molecular
(simple covalent)
has a definite number of atoms
strong attractions between atoms in the molecule (intra-molecular). weak attractions between molecules (inter-molecular).
Dative Covalent Bond
atoms attracted to shared pair of electrons, provided entirely by one of the atoms
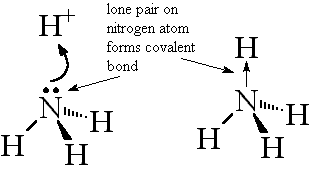
electronegativity is the power of an atom to attract electron density from a covalent bond
Fluorine has the highest electronegativity
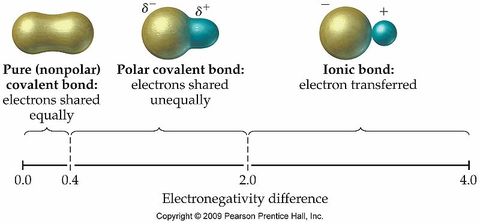
Polar Bonds
certain combinations cause electron pair to be closer to one of the atoms

Certain atom combinations of different electronegativity create stronger dipoles
Van Der Waal's attractions (vdW)
(London inter-molecular Forces)
There's a chance that electrons will be closer to one end of non-polar molecule than the other.
What does this suggest?
Hydrogen Bonds are in a way similar to dative covalent bonds. but these are much much weaker.
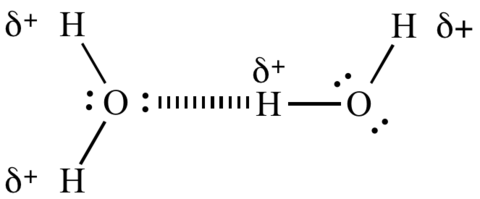
Carboxyllic Acid A has boiling point 170*
Same carbon chain length alkane B has boiling point of 80*
why is that?
ΔH
Symbol for enthalpy change.
Remember the units?
ΔH Cø
Enthalpy change when 1mol of substance has been combusted in excess oxygen
Ø(in standard conditions)
ΔH fø
Enthalpy change when 1mol of substance has been made from its constituent elements
Ø(in standard conditions)
q=mcΔT
meth- eth- pro- but- pent- hex-
the following (end Points) are on carbon 1
carboxyllic acid
nitrile group
aldehydes
amines
Fractional distillation works because....?
during Frac. Distillation we get lots of thick, long-chained groups.
how do we use these for better causes?
Zeolite catalyst-
looks like a lattice of donuts
produces chain-isomer alkanes + alkenes
how's this useful?
Zeolite cracking:
aromatic H-Carbons
Fuels
Many alkenes and ring carbons
H temp. M pressure. Zeo Catalyst
C(x)H(2x+2)
C2H5, C50H102, etc
can combust with O2
Car Fuels have impurities
sulfur and its oxides, carbon monoxide, methane, Nitrous oxides. We use platinum catalysts to remove these.
O2 reacts with them to form less harmful gasses
Hess' Law
remember it?
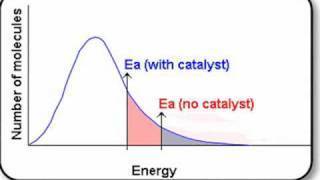
catalysts
what do they do?
Maxwell Boltzmann
Collision Theory
-ΔH reaction is exothermic
+ΔH reaction is endothermic
(endothermic is uncommon)
How do you increase rate of reaction?
(Or rate at which reaction reaches equilibrium?)
If a system at equilibrium is disturbed, conditions favor the reaction which tends to reduce the disturbance
Equilibrium is in closed system
You won't see an example where temperature or pressure are changing live, whilst reactions are underway
Mathematical Kc expression.
purely algebraic representation.
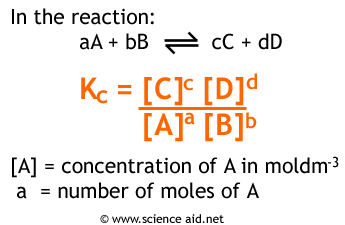
Kc = 0.00063652 when mostly reactants are present; its tiny.
Kc = 1254.95 when mostly products are present, it's massive
CH4(g) + 2H2O(g) <--> CO2(g) + 4H2(g)
Initially, 1.0 mol of methane and 2.0 mol of steam were placed in a flask and heated until equilibrium was established. The equilibrium mixture contained 0.25 mol of CO2.
a)i) Calculate the amounts, in moles, of methane, steam and hydrogen in the equilibrium mixture.
OIL RIG
Oxidation is Loss (of electrons)
Reduction is Gain (of electrons)
and when you cause it, you're its agent.
Common Oxidation States
group 1 metals +1
group 2 metals +2
Fluorine -1 .
Cl -1 (but work it out)
Oxygen -2 E.
Hydrogen +1 E.
make x2 half equations by considering both reactants separately.
Mathematical value Kc
Reacts to temperature only.
If pressure changes and more X is found at equilibrium, Kc does not change since it measures rate of reaction at equilibrium.
Group 7 Halogens
Are most electronegative. F is the best example. Why is that?
Testing for halogens using Silver Nitrate.
Remember the results?
Testing for halide ions (ii)
Add Silver Nitrate
(White, cream, yellow)
Then see if (Cl Br I) solute in ammonia.
What should happen?
We write compounds as
CH3CH2COOH
(Propanoic acid)
instead of C3H6O2
Displayed formula
In the old days, people had ratios of atoms to work with. they knew that (carbon is responsible for 63% of the mass, rest seems to be Hydrogen)
So we called that simplest ratio Empirical. Just like Americans love their inches, Chemists refuse to give up this ancient system. Comes in handy sometimes, it's obvious when it's needed.
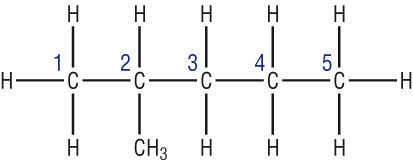
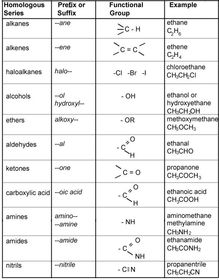
Carbon chain can be named.
name has a base: -Meth- -Eth- -Pro- -Bu-
name has a prefix for any appropriate groups: Methyl-, Hydroxy-
Name has a Suffix: -yde, -ol, -one, -al etc
Name's prefix has a rule: -between-numbers-&-words: 6-methyl
Alkanes are straight
AlkENEs have a Double bond
alkenes and (CycloAlkanes) have the same molecular formulae.
It took them wayyy too long to figure out that alkenes can become cyclic.
Nucleophiles really want to get rid of some of their electrons.
Electrophiles are twitchy, and will not stop until their electron-gain hunger is fulfilled.
How to know if reaction is Called NucleophillicX or ElectrophyllicX?
How to know if reaction is XSubstitution, or XAddition?
Elimination
Vicious reaction, in a hurling, swirling HOT ACID.
The poor alkane can't help but to loose H2 and form a double bond!
Infrared Spectrum-
each living bond absorbs a specific wavelength of infrared light.
which ranges in general does InfraRed spectrum show?
Remember good old
TOF Mass Spec.?
why do ions accelerate through drift region?
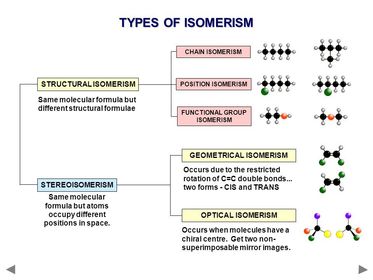
what are chain isomers?
what are position isomers?
What are functional group isomers?
What are optical E-Z isomers?
how would you know which group on a molecule is more important?
Testing for aldehyde in a mixture of alcohol, aldehyde and acid.
Test for Halide Ions
Mix with Acidified Silver Nitrate
(solubility- mix with Ammonia)

 Ocultar acertos
Ocultar acertos