GCSE Chemistry: The Crust
|
|
Created by Landon Valencia
over 9 years ago
|
|




 (0)
(0)
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 | ||
| 0 |
0 comments
There are no comments, be the first and leave one below:
Structure of the Earth
Add Title- crust - relatively thin and rocky
- mantle - has the properties of a solid, but can flow very slowly
- outer core - made from liquid nickel and iron
- Inner core - made from solid nickel and iron
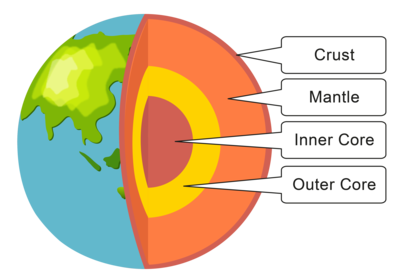 Cross section showing structure of the Earth
Cross section showing structure of the Earth
Continental Drift & Wegener’s Theory
Add TitleThe theory of continental drift was proposed at the beginning of the last century by German scientist Alfred Wegener.
Before Wegener developed his theory, it was thought that mountains formed because the Earth was cooling down, and, as it cooled down, it contracted This process formed wrinkles, or mountains, on the Earth’s crust.
If this was the case, then mountains would be spread evenly over the Earth's surface. We know that this is not the case.
Wegener suggested that mountains formed when the edge of a drifting continent collided with another, causing it to crumple and fold. For example, the Himalayas formed when India came into contact with Asia.
It took more than 50 years for Wegener’s theory to be accepted. One of the reasons was that it was difficult to work out how whole continents could move. It was not until the 1960s that enough evidence was discovered to support the theory fully.
Plate Tectonics
Add Title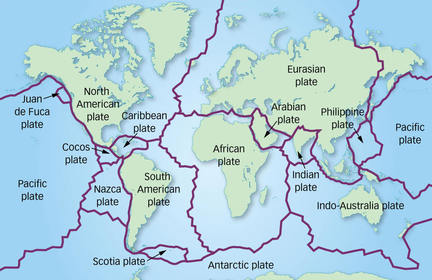 The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. Closely examine the map below, which shows the 15 major tectonic plates.
The earth's continents are constantly moving due to the motions of the tectonic plates. Closely examine the map below, which shows the 15 major tectonic plates.
The plates move because of convection currents in the Earth’s mantle. These are driven by the heat produced by the natural decay of radioactive elements in the Earth.
Where tectonic plates meet, the Earth's crust becomes unstable as the plates push against each other, or ride under or over each other. Earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen at the boundaries between plates, and the crust may ‘crumple’ to form mountain ranges.
Types of Rock
Add TitleIgneous Rock
Igneous Rocks are formed by magma from the molten interior of the Earth. When magma erupts it cools to form volcanic landforms.
When it cools inside the Earth it forms intrusive rock, which may later be exposed by erosion and weathering. Intrusive rock will have large crystals as it has cooled slowly. Magma that has cooled on the surface is known as extrusive rock. This will have small crystals as it has cooled quickly
Sedimentary Rocks
Add TitleA river carries, or transports, pieces of broken rock as it flows along. When the river reaches a lake or the sea, its load of transported rocks settles to the bottom. We say that the rocks are deposited. The deposited rocks build up in layers, called sediments. This process is called sedimentation.
The weight of the sediments on top squashes the sediments at the bottom. This is called compaction. The water is squeezed out from between the pieces of rock and crystals of different salts form.
These are the different processes in order:
sedimentation → compaction → cementation
Sedimentary rocks contain rounded grains in layers. Examples of sedimentary rock include: chalk, limestone, sandstone, shale Sedimentary rocks may contain fossils of animals and plants trapped in the sediments as the rock was formed. Sedimentary rocks are often quite soft and are susceptible to erosion.
Sedimentary rocks may contain fossils of animals and plants trapped in the sediments as the rock was formed. Sedimentary rocks are often quite soft and are susceptible to erosion.
Metamorphic Rocks
Add Titlehttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tI344TmxN-I Metamorphic Rocks
Metamorphic rock has been subjected to tremendous heat, pressure or both. This has caused it to change into another type of rock. It is usually resistant to weathering and erosion and is therefore very hard-wearing.
Examples of metamorphic rock include:
- marble - which originates from chalk or limestone
- slate - which originates from clay
- schists – which have formed from sandstone or shale (sedimentary rocks)
Quarrying
Add Title- it can be used as a building material
- it is a major ingredient in toothpaste
- it can be used as a food additive to provide calcium ions for strong teeth and bones
- it can be processed as a useful raw material in the chemical industry
Most limestone is obtained by quarrying, where the rock is blasted out of the ground in huge pits.
Uses of Limestone
Add TitleCarbonates react with acids to produce carbon dioxide, a salt and water. For example:
calcium carbonate + hydrochloric acid → carbon dioxide + calcium chloride + water
CaCO3(aq) + 2HCl(aq) → CO2(g) + CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l)
Since Limestone is mostly calcium carbonate, it is damaged by acid rain.
Calcium Hydroxide
Add Titlecalcium carbonate → calcium oxide + carbon dioxide
CaCO3(s) → CaO(s) + CO2(g)
This reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide, which is an alkali
calcium oxide + water → calcium hydroxide
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(s)
Calcium hydroxide is used to neutralise excess acidity, for example, in lakes and soils affected by acid rain. Calcium hydroxide dissolves in water to produce calcium hydroxide (limewater), which is used to test for carbon dioxide.
Cement, mortar and concrete
Add TitleCement is an ingredient in mortar and concrete. Mortar - used to join bricks together - is made by mixing cement with sand and water. Concrete is made by mixing cement with sand, water and aggregate (crushed rock).
Concrete is easily formed into different shapes before it sets hard. It is strong when squashed, but weak when bent or stretched. However, concrete can be made much stronger by reinforcing it with steel.
Limestone, cement and mortar slowly react with carbon dioxide dissolved in rainwater and wear away. This damages walls made from limestone, and leaves gaps between bricks in buildings. These gaps must be filled in or ‘pointed’.
Pollution from burning fossil fuels makes the rain more acidic than it should be, and this acid rain makes these problems worse.
